Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Do Dogs Get Ticks And Fleas


Common Health Issues
How Do Dogs Get Ticks And Fleas
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about common health issues for dogs, including how they get ticks and fleas. Find out how to protect your pet from these pests.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dogs are cherished members of countless families, bringing joy, companionship, and unwavering loyalty. However, these beloved pets are susceptible to various health issues, with ticks and fleas being among the most common concerns. These tiny parasites can cause discomfort, irritation, and even serious health problems for dogs. Therefore, it's crucial for dog owners to understand how these pests affect their furry friends and how to prevent and treat infestations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of ticks and fleas, exploring how dogs acquire these parasites, the potential health risks they pose, and effective strategies for prevention and treatment. By gaining a deeper understanding of these pesky critters and learning how to safeguard our canine companions, we can ensure that they lead happy, healthy lives free from the torment of ticks and fleas.
Throughout this article, we will provide valuable insights into the nature of ticks and fleas, shedding light on their life cycles, preferred habitats, and the manner in which they latch onto dogs. Additionally, we will offer practical advice on preventing infestations, including tips for maintaining a clean and pest-free environment for dogs. Furthermore, we will explore various treatment options, from topical solutions to oral medications, to help dog owners effectively combat ticks and fleas and alleviate their pets' discomfort.
By the end of this guide, readers will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to protect their furry companions from the perils of ticks and fleas. With a proactive approach to prevention and a thorough understanding of treatment options, dog owners can ensure that their pets remain happy, healthy, and free from the grasp of these troublesome parasites.
Read more: How Do Indoor Dogs Get Fleas
Understanding Ticks and Fleas
Ticks and fleas are common external parasites that pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of dogs. Understanding the nature of these pests is essential for effective prevention and treatment.
Ticks
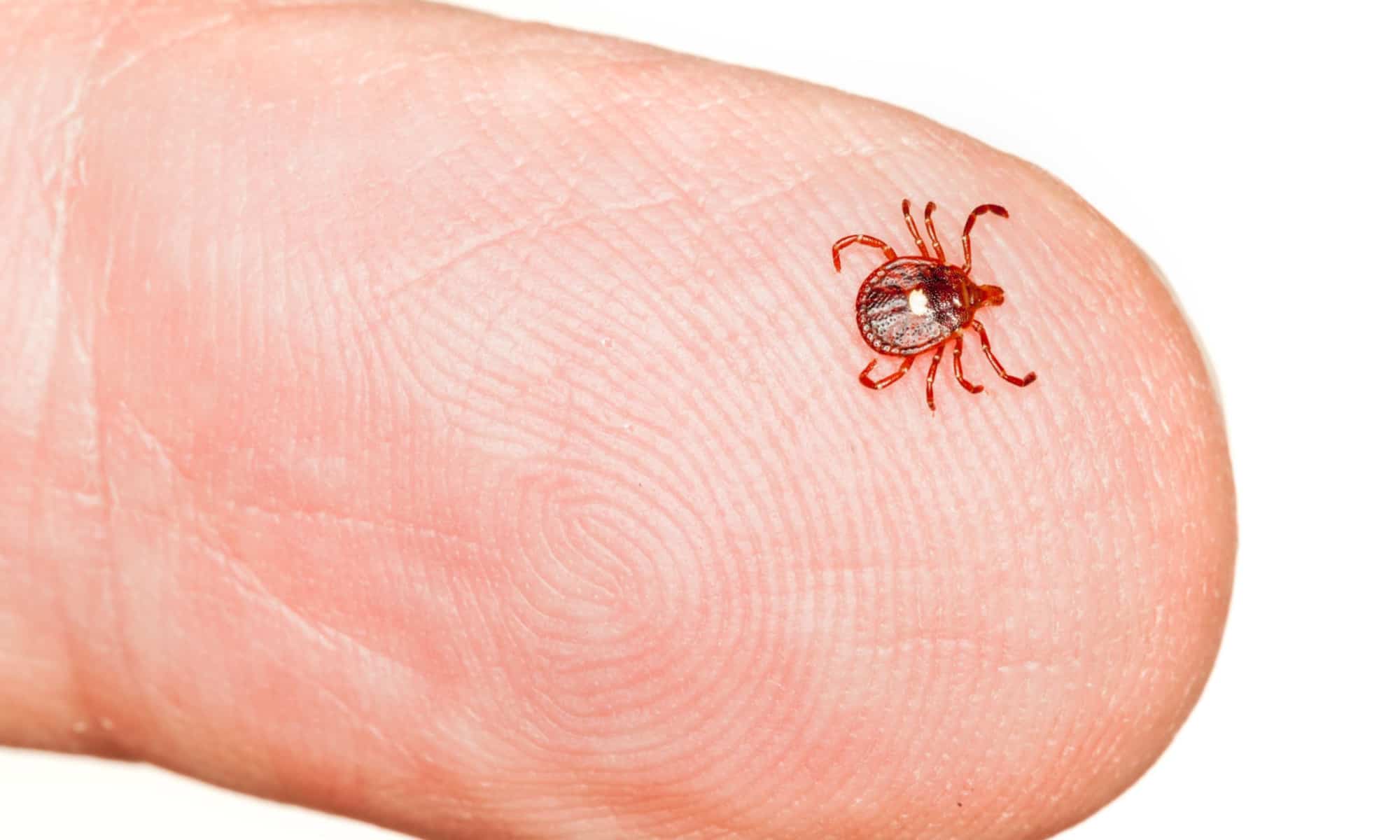
Ticks are arachnids belonging to the order Parasitiformes, known for their blood-feeding habits. These ectoparasites have a remarkable ability to detect hosts through sensory organs, such as Haller's organs, located on their front legs. Once a suitable host, such as a dog, is detected, ticks use their specialized mouthparts to anchor themselves firmly to the host's skin and begin feeding on blood.
Ticks undergo four life stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. During each stage, they require a blood meal to progress to the next phase of their life cycle. This dependency on blood makes dogs vulnerable to tick-borne diseases, as ticks can transmit various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, while feeding.
Fleas
Fleas, on the other hand, are wingless insects of the order Siphonaptera. These minuscule parasites possess powerful hind legs, enabling them to leap impressive distances relative to their size. Fleas are equipped with specialized mouthparts designed for piercing the skin and siphoning blood from their hosts.
Similar to ticks, fleas have a complex life cycle consisting of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Flea eggs are typically laid on the host but can easily fall off onto bedding, carpets, or outdoor areas frequented by the host. This characteristic contributes to the rapid spread of flea infestations within the dog's environment.
Understanding the life cycles and feeding behaviors of ticks and fleas is crucial for implementing effective control measures. By comprehending the habits and vulnerabilities of these parasites, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from infestations and the associated health risks.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore how dogs acquire ticks and fleas, as well as practical strategies for preventing and treating infestations, empowering dog owners to safeguard their beloved pets from these troublesome parasites.
How Dogs Get Ticks
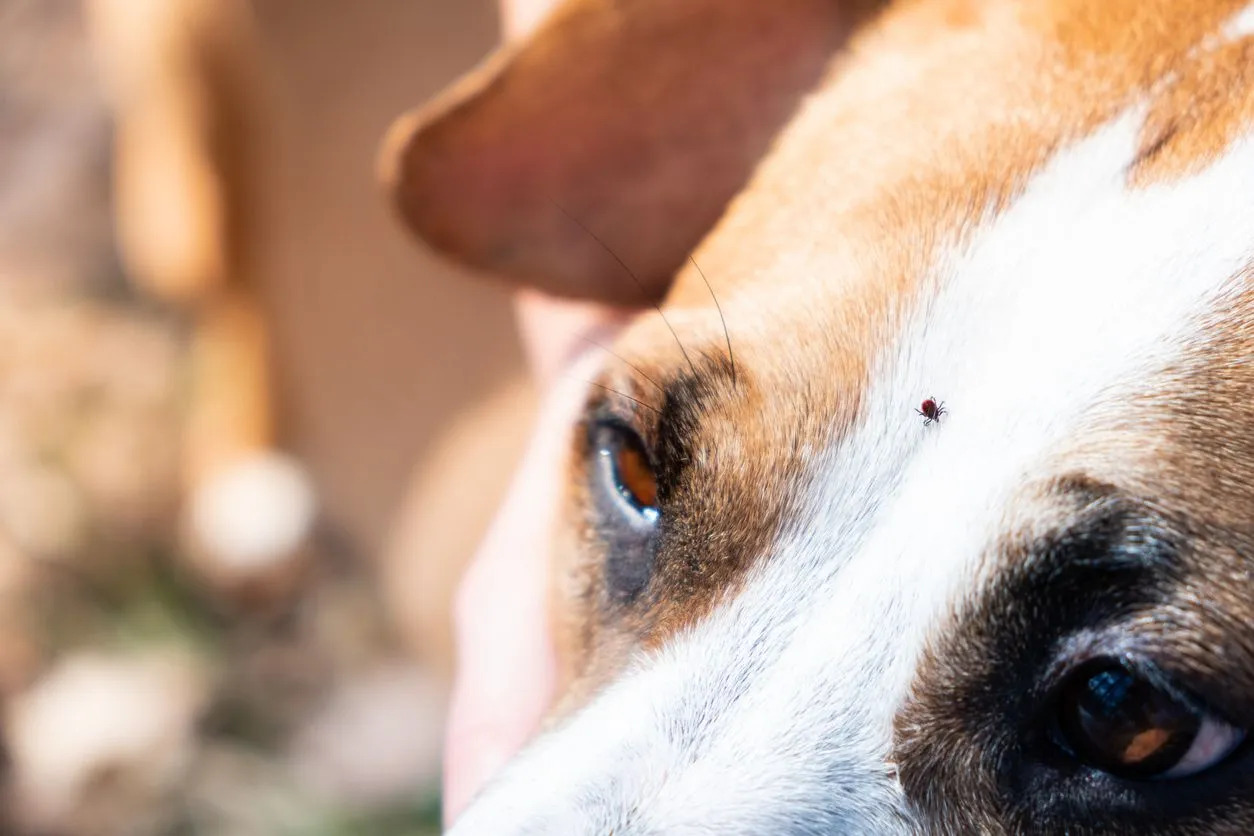
Ticks are notorious for their ability to latch onto unsuspecting hosts, including dogs, as they venture through outdoor environments. Understanding how dogs acquire ticks is essential for implementing preventive measures and minimizing the risk of infestation.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas And Ticks On My Dog
Outdoor Exposure
When dogs explore grassy, wooded, or overgrown areas, they become susceptible to encountering ticks. These parasites thrive in environments with dense vegetation and high humidity, making such locations prime habitats for ticks. As dogs navigate through these outdoor settings, ticks opportunistically latch onto their fur, seeking an ideal feeding site on the host's skin.
Contact with Infested Animals
Dogs can acquire ticks through interactions with other infested animals, such as wildlife or fellow pets. When dogs come into contact with infested creatures, ticks can easily transfer from one host to another. This transmission can occur during playful encounters, shared living spaces, or while exploring common outdoor territories.
Tick-Infested Environments
Ticks can lurk in various outdoor environments, including parks, hiking trails, and backyard spaces. When dogs frequent these areas, they may inadvertently pick up ticks from the surroundings. Additionally, ticks can hitch a ride into the home on humans' clothing or belongings, posing a risk of infestation within the domestic environment.
Seasonal Variations
The prevalence of ticks can fluctuate with seasonal changes. Warmer months, particularly spring and summer, often coincide with heightened tick activity. During these seasons, dogs are more likely to encounter ticks while spending time outdoors. However, it's important to note that ticks can remain active in milder climates and indoor environments throughout the year.
Read more: Where Do Dogs Get Ticks?
Tick-Prone Regions
Certain geographical regions are known for their elevated tick populations, increasing the likelihood of dogs acquiring these parasites. Wooded areas, grasslands, and regions with abundant wildlife can harbor substantial tick populations, posing a greater risk to dogs residing or exploring these environments.
By understanding the various ways in which dogs can acquire ticks, pet owners can take proactive measures to minimize their pets' exposure to these parasites. Through diligent tick checks, preventive treatments, and environmental management, dog owners can effectively safeguard their furry companions from the perils of tick infestations.
How Dogs Get Fleas
Fleas are notorious for their remarkable ability to infest dogs, causing discomfort and potential health issues. Understanding how dogs acquire fleas is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and minimizing the risk of infestation.
Contact with Infested Animals
Dogs can easily pick up fleas through interactions with infested animals, such as wildlife or other pets. When dogs come into contact with these creatures, fleas can quickly transfer from one host to another. This transmission can occur during playful encounters, shared living spaces, or while exploring common outdoor territories. Therefore, dogs that socialize with other animals, whether in the neighborhood or at parks, are at an increased risk of acquiring fleas.
Indoor Environments
Fleas can thrive in indoor environments, particularly in homes with carpeting, upholstery, and bedding. These parasites can hitch a ride into the home on clothing, shoes, or other belongings, allowing them to infest the indoor spaces where dogs reside. Additionally, fleas can lay eggs in the soft furnishings and crevices within the home, leading to rapid infestations that pose a significant challenge for dog owners.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas And Ticks On My Dog
Outdoor Exposure
When dogs spend time outdoors in areas frequented by wildlife or other infested animals, they become susceptible to flea infestations. Fleas can lurk in outdoor spaces such as parks, yards, and hiking trails, waiting to latch onto passing hosts. Moreover, outdoor environments with high humidity and moderate temperatures provide ideal conditions for fleas to thrive, increasing the likelihood of dogs acquiring these parasites during their outdoor adventures.
Seasonal Variations
Flea activity often peaks during warm and humid seasons, with spring and summer being particularly conducive to flea infestations. However, fleas can remain active in milder climates and indoor environments throughout the year. Therefore, dog owners should remain vigilant and proactive in implementing year-round flea prevention measures to protect their pets from infestations.
Flea-Prone Regions
Certain geographical regions with abundant wildlife and moderate climates are known for their elevated flea populations. Dogs residing or exploring these areas are at a higher risk of encountering fleas. Additionally, urban environments with a dense pet population can also harbor substantial flea infestations, posing a constant threat to dogs in these areas.
By understanding the various ways in which dogs can acquire fleas, pet owners can take proactive measures to minimize their pets' exposure to these parasites. Through regular grooming, preventive treatments, and meticulous household hygiene, dog owners can effectively safeguard their furry companions from the perils of flea infestations.
Preventing Ticks and Fleas
Preventing ticks and fleas is paramount in ensuring the well-being of dogs and maintaining a harmonious coexistence between pets and their owners. By implementing proactive measures, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of infestations and the associated health issues. Here are effective strategies for preventing ticks and fleas:
Read more: What Time Of Year Do Dogs Get Ticks
Regular Grooming
Frequent grooming sessions provide an excellent opportunity to inspect dogs for ticks and fleas. Thoroughly combing through the fur allows for the early detection and removal of these parasites before they can establish infestations. Additionally, bathing dogs with vet-recommended shampoos and grooming products can help repel ticks and fleas, contributing to a proactive preventive approach.
Environmental Management
Maintaining a clean and well-kept environment is crucial for preventing ticks and fleas. Regular vacuuming, washing pet bedding, and cleaning indoor spaces help eliminate flea eggs, larvae, and pupae, reducing the likelihood of infestations. Outdoor areas frequented by dogs should be kept free of overgrown vegetation and debris, minimizing tick habitats and lowering the risk of exposure.
Preventive Treatments
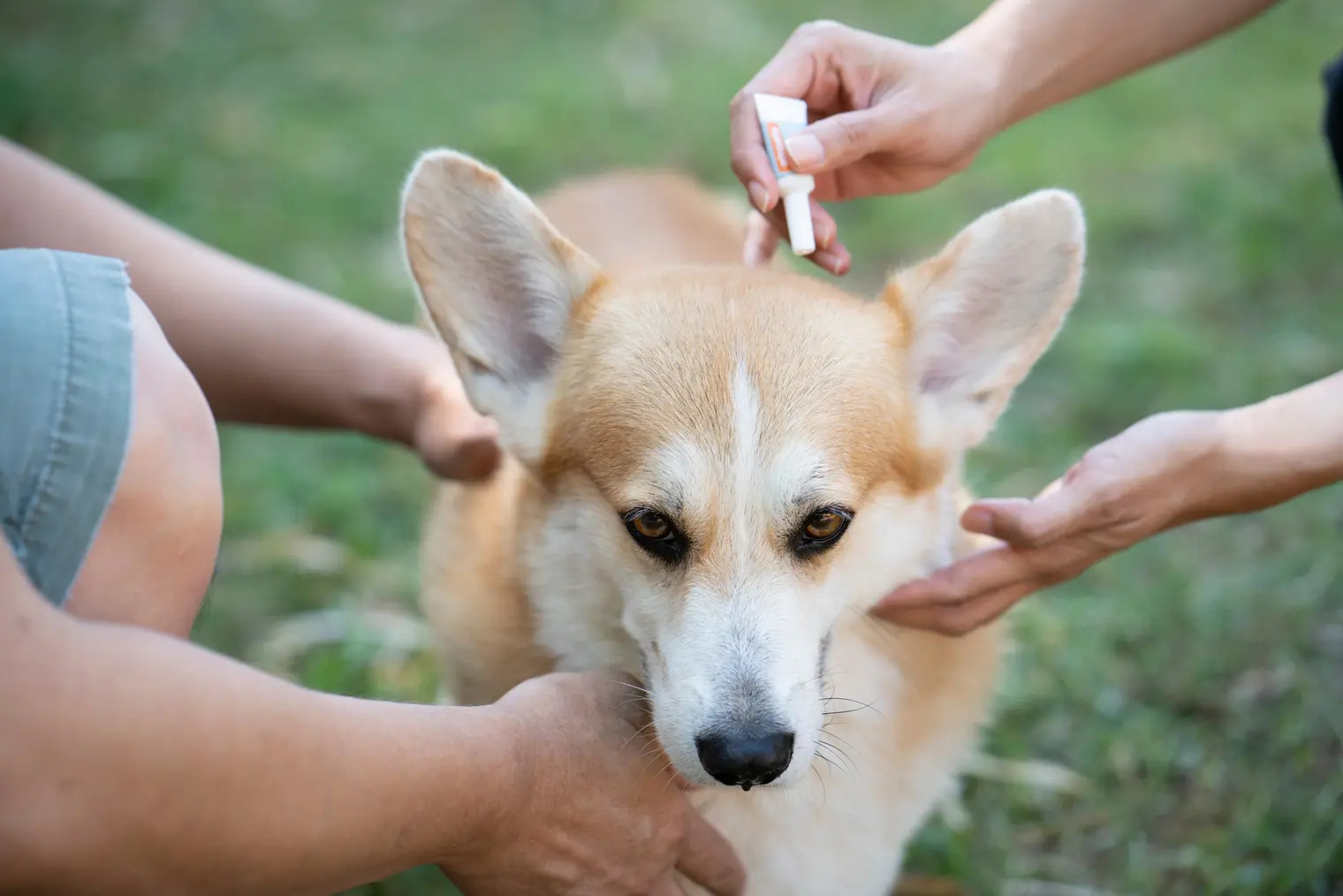
Utilizing veterinarian-recommended tick and flea preventive treatments is essential for long-term protection. These treatments include topical solutions, oral medications, and collars designed to repel and eliminate ticks and fleas. By adhering to a regular preventive treatment schedule, dog owners can effectively shield their pets from infestations and the potential health risks associated with these parasites.
Tick and Flea Control Products
Implementing tick and flea control products in the dog's environment can significantly reduce the risk of infestations. This includes using pet-safe sprays, powders, and foggers designed to eliminate ticks and fleas from indoor spaces. Additionally, yard treatments and outdoor sprays can help create a barrier against ticks and fleas, minimizing the likelihood of infestations originating from the outdoor environment.
Consultation with Veterinarians
Regular consultations with veterinarians are invaluable for devising personalized tick and flea prevention plans tailored to the specific needs of dogs. Veterinarians can recommend the most suitable preventive treatments, offer guidance on environmental management, and provide insights into the prevalence of ticks and fleas in the local area, empowering dog owners to make informed decisions regarding their pets' well-being.
By incorporating these preventive strategies into their routine care regimen, dog owners can effectively shield their beloved pets from the perils of ticks and fleas. Through a proactive and comprehensive approach to prevention, dogs can enjoy a pest-free existence, free from the discomfort and health risks posed by these troublesome parasites.
Treating Ticks and Fleas on Dogs
Effective treatment of ticks and fleas is essential for alleviating the discomfort and health risks posed to dogs by these troublesome parasites. By employing appropriate treatment methods, dog owners can eradicate existing infestations and prevent reinfestation, ensuring the well-being of their beloved pets.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as spot-on solutions and sprays, are commonly used to eliminate ticks and fleas on dogs. These products are applied directly to the dog's skin, typically between the shoulder blades, where they provide long-lasting protection against parasites. Topical treatments work by disrupting the life cycle of ticks and fleas, effectively killing existing parasites and preventing new infestations.
Oral Medications
Oral medications offer a convenient and effective approach to treating ticks and fleas in dogs. These medications are available in chewable tablet or pill form and are administered orally. Once ingested, the active ingredients circulate in the dog's bloodstream, effectively targeting ticks and fleas upon contact. Oral medications provide systemic protection, ensuring that parasites are eliminated throughout the dog's body.
Shampoos and Dips
Bathing dogs with medicated shampoos and dips can help eliminate ticks and fleas infesting their fur and skin. These products contain active ingredients that kill parasites on contact, providing immediate relief to infested dogs. Additionally, shampoos and dips can help soothe irritated skin and alleviate itching caused by tick and flea bites, promoting the dog's comfort and well-being.
Environmental Treatments
Treating the dog's environment is crucial for eradicating ticks and fleas and preventing reinfestation. Utilizing household sprays, foggers, and yard treatments can effectively eliminate parasites from indoor and outdoor spaces. These treatments target flea eggs, larvae, and pupae, disrupting the life cycle of parasites and creating a pest-free environment for dogs.
Professional Services
In severe infestation cases, seeking professional pest control services may be necessary to address persistent tick and flea problems. Pest control experts can conduct thorough treatments of the dog's environment, utilizing specialized products and techniques to eradicate parasites effectively. Additionally, veterinarians can provide guidance and support in managing severe infestations, ensuring the comprehensive treatment of affected dogs.
By employing a combination of these treatment methods and adhering to a consistent treatment schedule, dog owners can effectively eliminate ticks and fleas, providing their pets with relief from the discomfort and health risks associated with parasite infestations. Additionally, integrating preventive measures into the dog's routine care regimen can help maintain a pest-free environment, ensuring the long-term well-being of dogs and fostering a harmonious relationship between pets and their owners.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ticks and fleas pose significant health risks to dogs, ranging from discomfort and irritation to the transmission of serious diseases. Understanding how dogs acquire these parasites and implementing effective preventive measures is crucial for safeguarding the well-being of our beloved pets.
By gaining insights into the life cycles and behaviors of ticks and fleas, dog owners can proactively protect their furry companions from infestations. Regular grooming, environmental management, and the use of preventive treatments are essential components of a comprehensive tick and flea prevention strategy. These measures not only minimize the risk of infestations but also contribute to the overall health and comfort of dogs.
In the event of tick or flea infestations, prompt and appropriate treatment is vital. Utilizing topical treatments, oral medications, and environmental treatments can effectively eradicate parasites and provide relief to infested dogs. Additionally, maintaining a clean and pest-free environment through regular household hygiene and yard treatments is essential for preventing reinfestation.
It is important for dog owners to consult with veterinarians to devise personalized tick and flea prevention plans tailored to the specific needs of their pets. Veterinarians can offer valuable guidance on preventive treatments, environmental management, and the prevalence of ticks and fleas in the local area, empowering dog owners to make informed decisions regarding their pets' well-being.
By integrating preventive measures and prompt treatment into their routine care regimen, dog owners can ensure that their pets lead happy, healthy lives free from the torment of ticks and fleas. Through vigilance, proactive measures, and a deep understanding of these troublesome parasites, we can provide our canine companions with a safe and comfortable environment, allowing them to thrive and enrich our lives with their boundless love and companionship.