Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>How To Conduct An Eye Exam On A Dog


Eye and Ear Health
How To Conduct An Eye Exam On A Dog
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn how to conduct a thorough eye exam on your dog to ensure their eye and ear health. Follow these expert tips for a successful examination.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to our furry friends, their health and well-being are of utmost importance. Just like humans, dogs can experience a range of eye and ear health issues that require attention and care. Conducting regular eye exams on dogs is crucial for maintaining their overall health and ensuring they have a good quality of life.
Dogs rely heavily on their senses, including their vision and hearing, to navigate the world around them. As responsible pet owners, it is our duty to monitor and address any potential issues that may arise in these areas. By conducting routine eye exams, we can detect early signs of eye diseases, infections, or injuries, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essential steps for conducting a thorough eye exam on a dog. From preparing for the exam to assessing visual function and considering additional tests, we will cover all aspects of this vital process. By understanding the key components of a dog's eye exam, pet owners and veterinary professionals can work together to ensure the best possible care for our beloved canine companions.
Read more: How To Conduct A Dog Allergy Food Trial
Preparing for the Exam
Before embarking on a comprehensive eye exam for your canine companion, it's essential to make adequate preparations to ensure a smooth and effective process. Here's a detailed look at the crucial steps involved in preparing for the exam:
-
Gather Necessary Equipment: Assemble all the essential tools and equipment required for the eye exam. This may include a penlight or ophthalmoscope for illuminating the eyes, a magnifying glass for close inspection, and sterile saline solution for rinsing the eyes if needed. Having these items readily available will streamline the examination process and allow for thorough assessments.
-
Create a Calm Environment: Dogs can be sensitive to their surroundings, especially when it comes to medical procedures. Choose a quiet and comfortable area for the exam, free from distractions and loud noises. Creating a calming environment will help reduce your dog's anxiety and facilitate a more cooperative demeanor during the examination.
-
Establish Trust and Comfort: Prior to the exam, spend some time with your dog to help them relax and feel at ease. Offer gentle reassurance and positive reinforcement to build trust and comfort. This can be achieved through soothing words, gentle petting, and the provision of favorite treats. A relaxed and trusting demeanor in your dog will contribute to a more successful and stress-free exam experience.
-
Review Medical History: Take a moment to review your dog's medical history, particularly any previous eye or ear issues, surgeries, or medications. Understanding your dog's health background will provide valuable insights and help direct the focus of the examination. Additionally, if your dog has been exhibiting specific symptoms related to their eyes or ears, make note of these for discussion with the veterinarian.
-
Secure Assistance if Needed: Depending on the size and temperament of your dog, it may be beneficial to have an extra pair of hands available to assist during the exam. This can be particularly helpful when conducting certain maneuvers that require steady positioning or when handling a more anxious or excitable dog. Enlist the help of a family member or friend to support you in ensuring a thorough and safe examination process.
By diligently preparing for the eye exam, pet owners can set the stage for a productive and insightful assessment of their dog's eye and ear health. These preparatory measures lay the foundation for a positive and effective examination experience, ultimately contributing to the overall well-being of our beloved canine companions.
Conducting the Physical Exam
The physical exam is a crucial component of assessing a dog's eye and ear health. It involves a systematic and thorough evaluation of the external structures of the eyes and ears, as well as the surrounding areas. Here's a detailed breakdown of the essential steps involved in conducting the physical exam:
-
External Inspection: Begin by visually examining the dog's eyes and ears. Look for any signs of redness, swelling, discharge, or abnormal growths. Check for crustiness around the eyes or ears, which may indicate the presence of discharge or dried secretions. Additionally, observe the dog's behavior for any signs of discomfort, such as excessive rubbing or scratching of the eyes or ears.
-
Palpation: Gently palpate around the eyes and ears to assess for any tenderness, lumps, or abnormalities. Use a gentle touch to avoid causing discomfort to the dog. Pay close attention to the dog's reactions during palpation, as any signs of pain or discomfort may indicate underlying issues that require further investigation.
-
Eye Movement and Reflexes: Evaluate the dog's eye movement and reflexes by observing their response to visual stimuli. Use a small object or your fingers to elicit a blink reflex and assess the dog's ability to track moving objects. Smooth and coordinated eye movements are indicative of normal visual function.
-
Ear Examination: When examining the ears, carefully inspect the external ear canal for any signs of inflammation, discharge, or foul odor. Gently lift the ear flaps to visualize the ear canal and check for the presence of excessive wax buildup or foreign objects. Take note of any discomfort or sensitivity expressed by the dog during this process.
-
Assessment of Pupillary Response: Use a penlight to assess the dog's pupillary response. Shine the light into each eye separately and observe the constriction and dilation of the pupils. A normal pupillary response is characterized by equal and brisk reactions in both eyes.
-
Evaluation of Tear Production: Assess tear production by observing the moisture level of the eyes. Normal tear production is essential for maintaining eye health and preventing dryness or irritation. Look for excessive tearing or, conversely, signs of insufficient tear production.
By meticulously conducting the physical exam, pet owners and veterinary professionals can gain valuable insights into the overall health and well-being of a dog's eyes and ears. This thorough assessment sets the stage for further investigations and interventions, if necessary, to address any identified issues and ensure optimal eye and ear health for our beloved canine companions.
Assessing Visual Function
Assessing a dog's visual function is a critical aspect of an eye exam, providing valuable insights into their overall ocular health and visual acuity. Understanding the methods for evaluating visual function in dogs is essential for detecting potential issues and ensuring optimal eye care. Here's a detailed exploration of the key elements involved in assessing a dog's visual function:
Observation of Behavior and Responses
Begin by observing the dog's behavior and responses to visual stimuli in various environments. Note how they navigate their surroundings, interact with objects, and respond to movements. Dogs with normal visual function exhibit keen awareness of their environment, track moving objects, and display appropriate reactions to visual cues.
Visual Acuity Testing
Visual acuity testing involves assessing the dog's ability to see and distinguish objects at various distances. This can be achieved through simple exercises such as tossing a small toy or treat and observing the dog's ability to locate and retrieve it. Additionally, observing the dog's response to hand gestures or subtle visual cues can provide insights into their visual acuity and depth perception.
Tracking and Following Movements
Evaluate the dog's ability to track and follow moving objects, such as a toy or a person's hand movements. Smooth and coordinated eye movements, along with accurate tracking of objects, indicate normal visual function. Any signs of difficulty in tracking or following movements may warrant further investigation into potential visual impairments.
Pupillary Light Reflex
Assess the dog's pupillary light reflex by shining a penlight into each eye separately. Observe the pupillary constriction and dilation in response to the light stimulus. A brisk and equal pupillary response in both eyes indicates normal neurological function and proper visual processing.
Visual Obstacle Course
Create a simple obstacle course with visual barriers and objects of varying heights and textures. Observe how the dog navigates the course, noting their ability to detect and maneuver around obstacles. This exercise provides valuable insights into the dog's depth perception, spatial awareness, and overall visual coordination.
By systematically assessing a dog's visual function through these methods, pet owners and veterinary professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the dog's ocular health and visual capabilities. This thorough evaluation serves as a cornerstone for identifying potential visual impairments, guiding treatment strategies, and promoting the overall well-being of our canine companions.
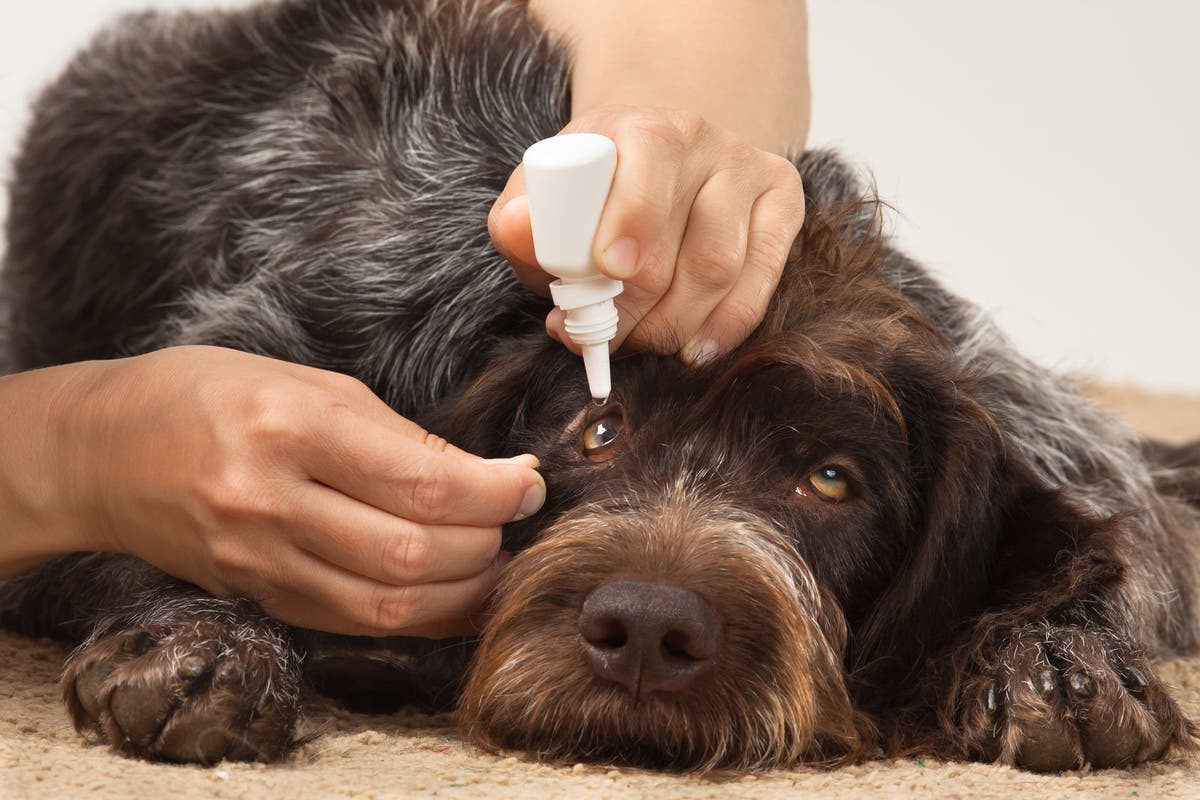
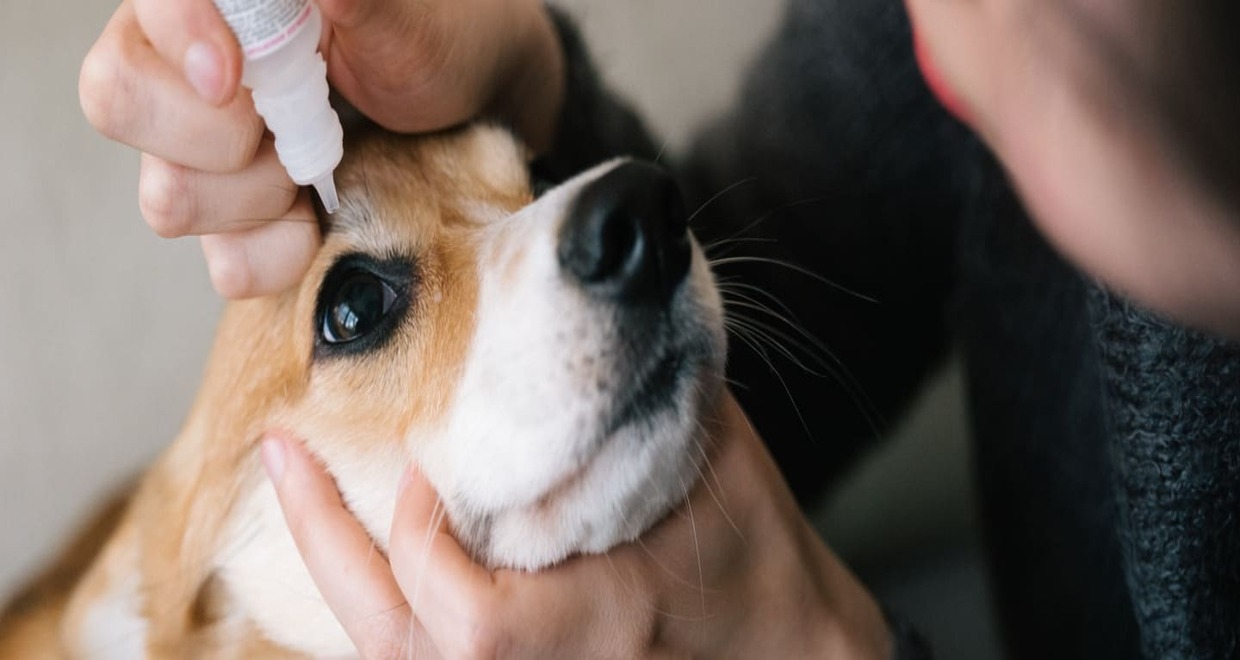
Read more: How To Give A Dog Eye Drops
Additional Tests and Considerations
In addition to the physical examination and assessment of visual function, there are several additional tests and considerations that play a crucial role in ensuring comprehensive eye and ear health for dogs. These supplementary evaluations provide valuable insights into specific aspects of ocular and auditory well-being, allowing for a more thorough understanding of any underlying issues or potential risks. Here's a detailed exploration of the additional tests and considerations that contribute to a holistic approach to canine eye and ear health:
Tonometry for Intraocular Pressure
Tonometry is a diagnostic test used to measure the intraocular pressure within a dog's eyes. Elevated intraocular pressure can be indicative of conditions such as glaucoma, which can pose serious threats to a dog's vision. By utilizing tonometry, veterinary professionals can assess the pressure within the eyes and identify any abnormalities that may require further intervention or management.
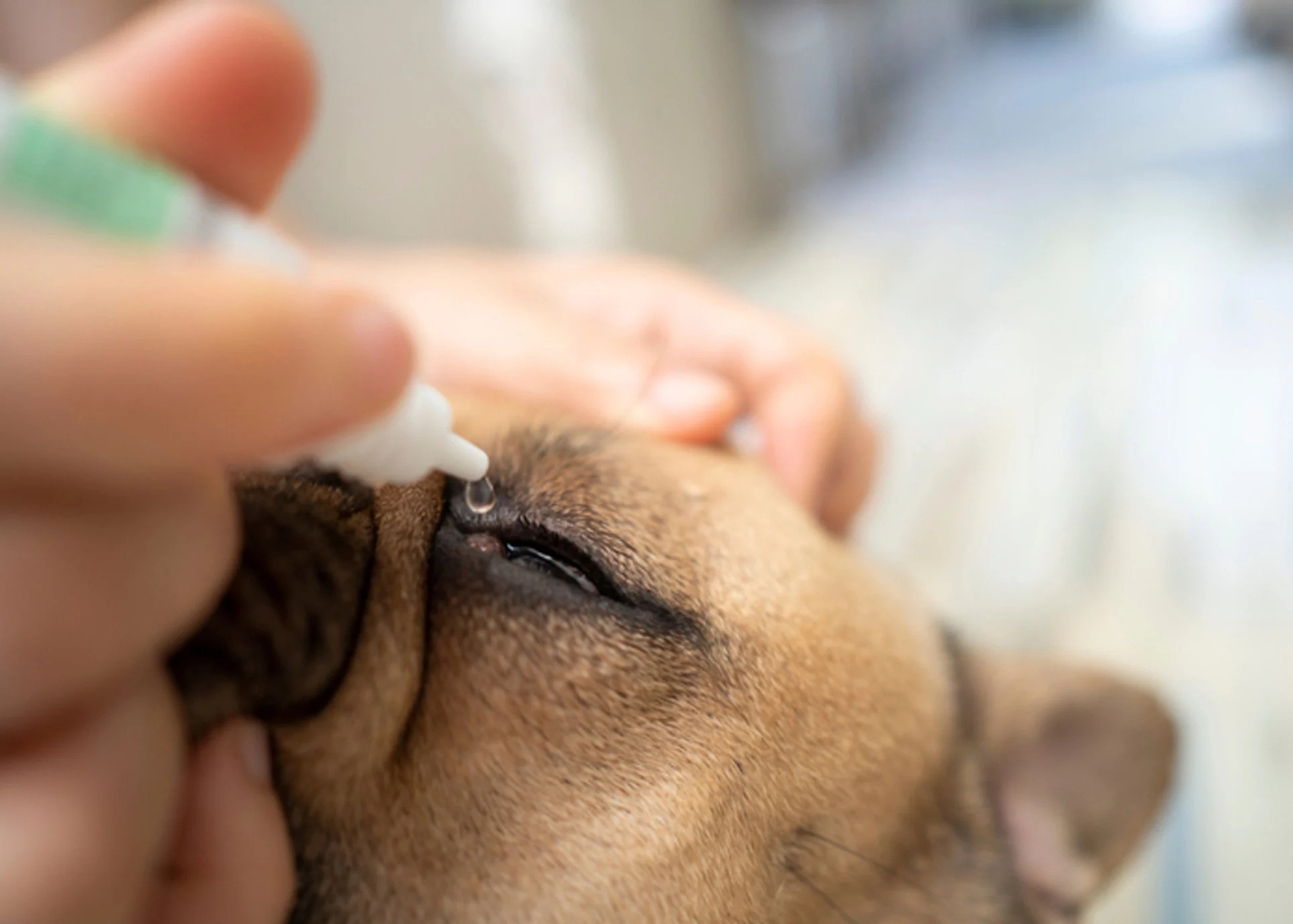
Fluorescein Staining for Corneal Injuries
Fluorescein staining is a valuable diagnostic tool for detecting corneal injuries or abrasions in dogs. By applying a small amount of fluorescein dye to the surface of the eye, veterinary professionals can identify areas of the cornea where the epithelial layer may be compromised. This test aids in the prompt diagnosis and treatment of corneal injuries, preventing potential complications and promoting optimal healing.
Schirmer Tear Test for Tear Production
The Schirmer tear test is employed to measure the production of tears in a dog's eyes. Adequate tear production is essential for maintaining ocular health and preventing conditions such as dry eye syndrome. By quantifying tear production through the Schirmer test, veterinary professionals can identify abnormalities and implement appropriate measures to address insufficient tear production and mitigate associated risks.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Mites By A Dog’s Eye
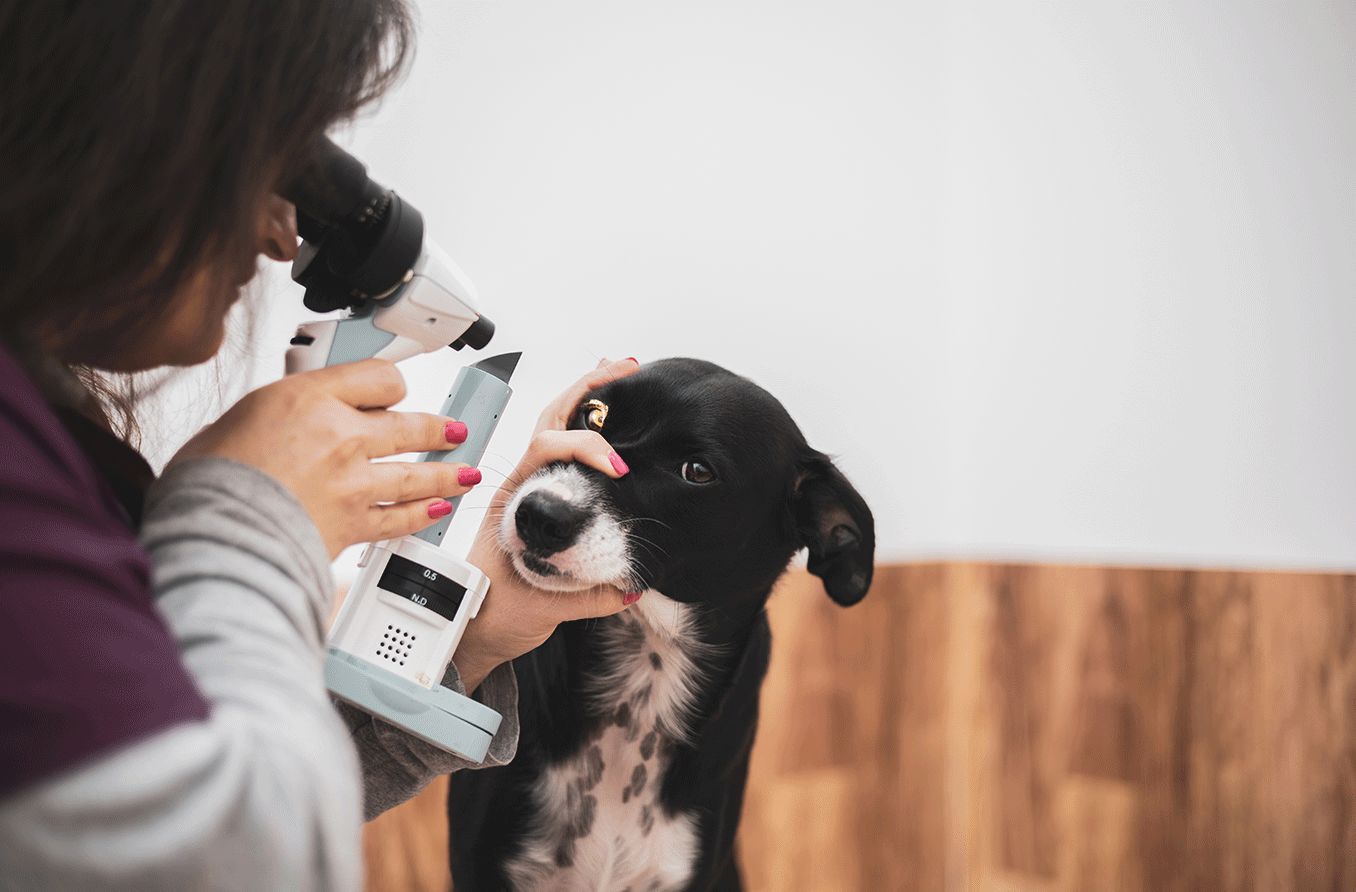
Otoscopic Examination for Ear Health
An otoscopic examination is a fundamental component of assessing a dog's ear health. This diagnostic procedure involves the use of an otoscope to visualize the external ear canal and the eardrum. Through otoscopy, veterinary professionals can identify signs of inflammation, ear infections, foreign objects, or other abnormalities that may impact a dog's auditory health. This examination is essential for detecting and addressing ear-related issues promptly.
Consideration of Breed-Specific Risks
Certain dog breeds are predisposed to specific eye and ear health concerns due to genetic factors or breed characteristics. For example, brachycephalic breeds may be more susceptible to ocular issues such as corneal ulcers or entropion, while dogs with pendulous ears, such as Basset Hounds, may be prone to ear infections. Understanding breed-specific risks enables veterinary professionals and pet owners to proactively address potential health challenges and implement targeted preventive measures.
By incorporating these additional tests and considerations into the evaluation of a dog's eye and ear health, pet owners and veterinary professionals can adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach to maintaining optimal ocular and auditory well-being. These supplementary assessments contribute to early detection, tailored interventions, and the promotion of long-term health for our beloved canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, conducting a thorough eye exam on a dog is an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership and proactive veterinary care. By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, pet owners and veterinary professionals can gain valuable insights into a dog's eye and ear health, enabling early detection of potential issues and the implementation of targeted interventions.
The process begins with meticulous preparation, including gathering necessary equipment, creating a calm environment, establishing trust and comfort, reviewing the dog's medical history, and securing assistance if needed. These preparatory measures set the stage for a productive and insightful examination experience, fostering a positive and cooperative demeanor in the dog.
The physical exam plays a pivotal role in assessing the external structures of the eyes and ears, evaluating eye movement and reflexes, and palpating for any abnormalities. This systematic evaluation provides valuable information about the overall health and well-being of a dog's eyes and ears, guiding further investigations and interventions as necessary.
Assessing a dog's visual function involves observing behavior and responses, testing visual acuity, evaluating pupillary light reflex, and creating visual obstacle courses. These methods offer a comprehensive understanding of a dog's ocular health and visual capabilities, facilitating the early detection of potential visual impairments and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Furthermore, additional tests and considerations, such as tonometry for intraocular pressure, fluorescein staining for corneal injuries, Schirmer tear tests for tear production, and otoscopic examinations for ear health, contribute to a holistic approach to canine eye and ear health. Understanding breed-specific risks further enables proactive measures to address potential health challenges in specific dog breeds.
By incorporating these comprehensive steps and considerations into the care regimen for our beloved canine companions, we can ensure that their eye and ear health is prioritized and maintained at an optimal level. Regular eye exams, coupled with attentive monitoring and prompt veterinary attention, contribute to the overall well-being and quality of life for our furry friends, allowing them to experience the world with clarity and comfort.
In essence, the commitment to proactive eye and ear care for dogs reflects our dedication to providing them with the best possible quality of life, ensuring that they can continue to delight us with their boundless energy, playful antics, and unwavering companionship for years to come.