Home>Health & Wellness>Nutrition & Diet>What Dog Diet Helps Stop Pancreatitis


Nutrition & Diet
What Dog Diet Helps Stop Pancreatitis
Published: January 27, 2024
Discover the best dog diet to prevent pancreatitis with proper nutrition and diet. Learn how to keep your dog healthy and happy with the right dietary choices.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to our furry companions, ensuring their well-being is a top priority. One common health concern among dogs is pancreatitis, a condition that can cause discomfort and distress. As pet owners, understanding the role of diet in preventing pancreatitis is crucial for maintaining the overall health of our beloved pets.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate relationship between diet and pancreatitis in dogs. By gaining insights into the impact of nutrition on this condition, pet owners can make informed decisions to support their dog's health and well-being.
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the pancreas, an organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and insulin. When the pancreas becomes inflamed, it can lead to various symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, pancreatitis can pose a significant threat to a dog's health, requiring immediate medical attention.
Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to pancreatitis is essential for devising preventive measures. While genetics and certain medical conditions can predispose a dog to pancreatitis, dietary choices play a pivotal role in mitigating the risk. By examining the impact of different nutrients and food components on the pancreas, pet owners can proactively tailor their dog's diet to reduce the likelihood of pancreatitis.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore the recommended diet for dogs to prevent pancreatitis, along with valuable insights into foods to avoid for dogs prone to this condition. Additionally, we will provide practical tips for feeding a dog with a history of pancreatitis, empowering pet owners with actionable strategies to support their pet's digestive health.
By delving into the intricate interplay between diet and pancreatitis, pet owners can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to make informed dietary choices for their furry companions. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the significance of a well-balanced diet in safeguarding our dogs against the perils of pancreatitis.
Understanding Pancreatitis in Dogs
Pancreatitis is a prevalent and potentially serious health condition that can affect dogs of all breeds and ages. This inflammatory disorder targets the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and regulating blood sugar levels through insulin secretion. When the pancreas becomes inflamed, it can lead to a cascade of distressing symptoms, ranging from abdominal pain and vomiting to loss of appetite and lethargy.
The underlying causes of pancreatitis in dogs can vary, encompassing a spectrum of factors such as dietary indiscretions, obesity, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Dietary indiscretions, such as consuming high-fat meals or scavenging from the trash, are recognized as common triggers for pancreatitis. Additionally, obesity is a significant risk factor, as excess body fat can contribute to metabolic imbalances and predispose the pancreas to inflammation.
The clinical manifestations of pancreatitis can manifest in varying degrees of severity, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Dogs with pancreatitis may exhibit symptoms such as abdominal tenderness, hunched posture, vomiting, diarrhea, and reluctance to eat. In severe cases, the condition can lead to systemic complications, including organ failure and shock, necessitating prompt veterinary intervention.
Diagnosing pancreatitis in dogs typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, encompassing physical examination, blood tests, and diagnostic imaging such as ultrasound. These diagnostic modalities enable veterinarians to assess the extent of pancreatic inflammation and identify potential complications, guiding the formulation of an appropriate treatment plan.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of pancreatitis in dogs is pivotal for pet owners, as it underscores the importance of proactive measures to mitigate the risk of this condition. By recognizing the potential triggers and symptoms of pancreatitis, pet owners can adopt a preventive approach, encompassing dietary modifications and lifestyle adjustments to safeguard their dog's pancreatic health.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the pivotal role of diet in preventing pancreatitis, shedding light on the recommended dietary strategies and foods to avoid. By unraveling the intricate interplay between nutrition and pancreatic health, pet owners can empower themselves with the knowledge needed to optimize their dog's diet and promote overall well-being.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Pancreatitis
Diet plays a pivotal role in preventing pancreatitis in dogs, serving as a cornerstone of proactive management to mitigate the risk of this inflammatory condition. By understanding the intricate interplay between nutrition and pancreatic health, pet owners can implement targeted dietary strategies to support their dog's well-being.
One of the primary dietary considerations in preventing pancreatitis involves regulating the fat content in a dog's diet. High-fat meals have been implicated as a significant trigger for pancreatitis, potentially inducing pancreatic inflammation and digestive disturbances. As such, opting for a balanced and moderate-fat diet is essential for reducing the likelihood of pancreatitis. By prioritizing lean protein sources and incorporating healthy fats in controlled amounts, pet owners can help maintain a harmonious balance in their dog's diet, minimizing the risk of pancreatic stress.
Moreover, the quality and composition of carbohydrates in a dog's diet can also influence pancreatic health. Complex carbohydrates, derived from sources such as whole grains and vegetables, offer sustained energy release and promote digestive wellness. By contrast, excessive consumption of simple carbohydrates, such as refined grains and sugary treats, can exert metabolic strain and potentially impact pancreatic function. Therefore, emphasizing complex carbohydrates as a staple component of a dog's diet can contribute to overall metabolic equilibrium and reduce the risk of pancreatitis.
In addition to fat and carbohydrate considerations, the role of dietary protein in preventing pancreatitis warrants attention. Opting for high-quality, easily digestible protein sources can support optimal pancreatic function and overall digestive health in dogs. By prioritizing lean meats and wholesome protein sources, pet owners can provide their dogs with essential nutrients while minimizing the potential burden on the pancreas.
Furthermore, the incorporation of dietary antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients can confer protective benefits for the pancreas. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as blueberries, spinach, and carrots, can help combat oxidative stress and bolster the body's natural defense mechanisms. Similarly, integrating omega-3 fatty acids, renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties, can contribute to a balanced inflammatory response, potentially mitigating the risk of pancreatic inflammation.
By recognizing the profound impact of diet on pancreatic health, pet owners can proactively tailor their dog's nutrition to align with preventive measures against pancreatitis. Through a holistic approach encompassing balanced fat intake, wholesome carbohydrates, quality protein sources, and supportive nutrients, pet owners can optimize their dog's diet to promote pancreatic wellness and overall vitality.
Recommended Diet for Dogs to Prevent Pancreatitis
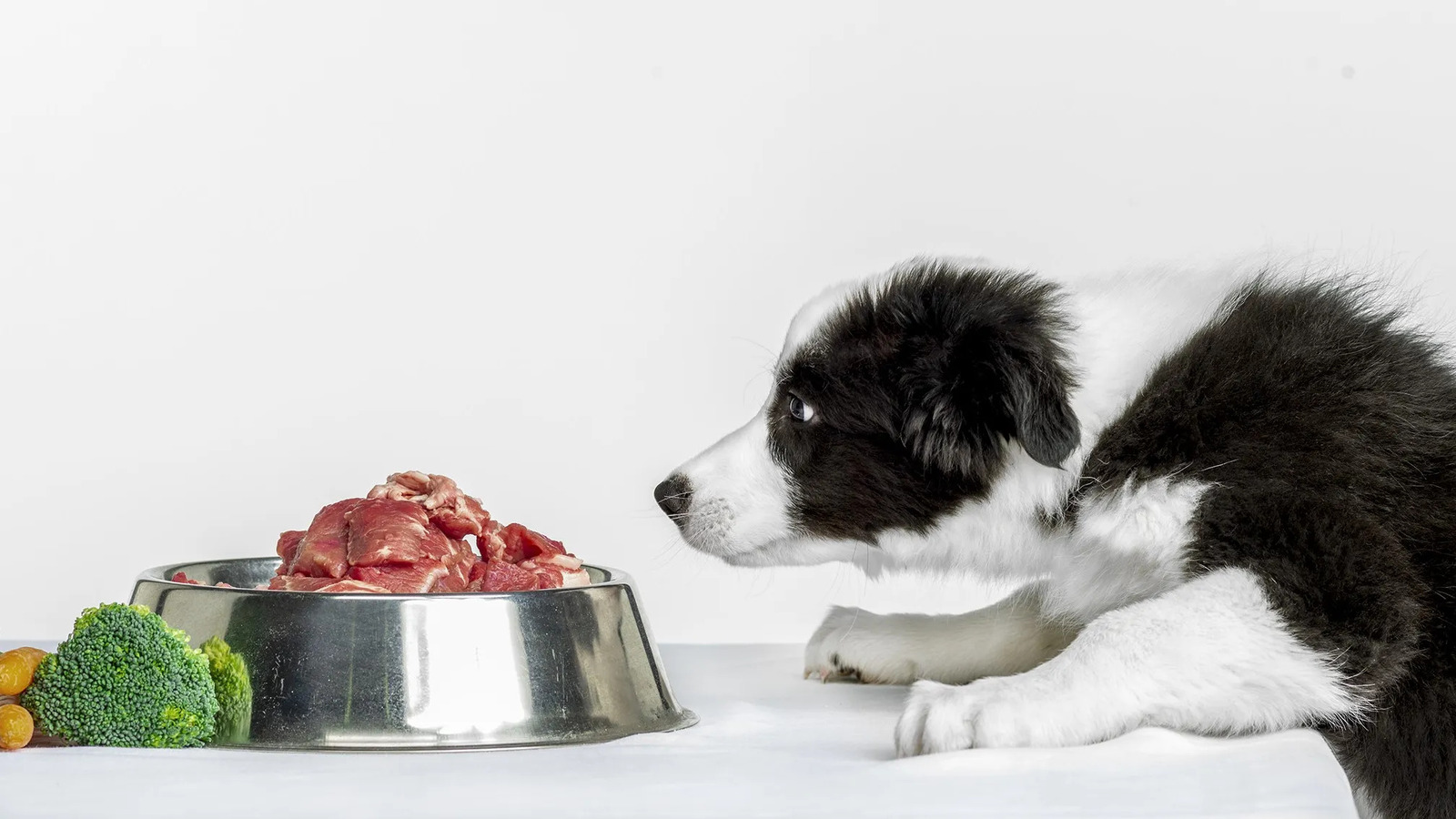
When formulating a diet to prevent pancreatitis in dogs, prioritizing a balanced and wholesome approach is paramount. Opting for a diet that emphasizes lean protein sources, moderate fat content, and complex carbohydrates can significantly contribute to mitigating the risk of pancreatic inflammation and promoting overall digestive wellness.
Lean Protein Sources
Incorporating lean protein sources, such as skinless poultry, lean cuts of beef, and fish, forms the cornerstone of a pancreatitis-preventive diet for dogs. These protein sources offer essential amino acids vital for muscle maintenance and overall health, while minimizing the potential burden on the pancreas. By prioritizing lean proteins, pet owners can provide their dogs with the necessary nutrients without compromising digestive equilibrium.
Read more: What Kind Of Diet Helps My Dog’s Itchy Skin
Moderate Fat Intake
Regulating fat intake is pivotal in preventing pancreatitis, as high-fat meals have been implicated as a significant trigger for this condition. Opting for moderate-fat diets, characterized by healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids from sources like fish oil, can support overall metabolic balance and reduce the likelihood of pancreatic stress. By steering clear of excessive fat consumption and focusing on quality fats, pet owners can safeguard their dog's pancreatic health.
Emphasis on Complex Carbohydrates
Incorporating complex carbohydrates from sources such as whole grains, sweet potatoes, and legumes can provide sustained energy release and promote digestive wellness. These carbohydrates offer valuable nutrients and fiber, supporting optimal gastrointestinal function while minimizing metabolic strain. By prioritizing complex carbohydrates over simple, refined grains, pet owners can contribute to a balanced and pancreatitis-preventive diet for their dogs.
Nutrient-Dense Foods
Integrating nutrient-dense foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties can confer protective benefits for the pancreas. Foods such as blueberries, spinach, and carrots, known for their antioxidant content, can help combat oxidative stress and bolster the body's natural defense mechanisms. Additionally, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids from sources like salmon and flaxseed can contribute to a balanced inflammatory response, potentially reducing the risk of pancreatic inflammation.
By aligning with these dietary recommendations, pet owners can proactively support their dog's digestive health and mitigate the risk of pancreatitis. Prioritizing a well-rounded diet that emphasizes lean protein sources, controlled fat intake, complex carbohydrates, and nutrient-dense foods can serve as a cornerstone for preventing pancreatitis and promoting overall well-being in dogs.
Foods to Avoid for Dogs Prone to Pancreatitis
When considering the dietary management of dogs prone to pancreatitis, it is imperative to identify and eliminate potential triggers that can exacerbate the risk of pancreatic inflammation. By steering clear of certain foods known to instigate pancreatic stress, pet owners can proactively safeguard their dog's well-being and reduce the likelihood of pancreatitis flare-ups.
-
High-Fat Foods: Foods rich in fat content, such as fatty cuts of meat, fried dishes, and greasy snacks, should be strictly avoided for dogs prone to pancreatitis. High-fat meals can impose a significant burden on the pancreas, potentially triggering inflammation and digestive distress. Opting for lean protein sources and minimizing fat intake is essential for mitigating the risk of pancreatic stress.
-
Fatty Meats: Fatty meats, including processed meats and cuts with visible marbling, should be excluded from the diet of dogs prone to pancreatitis. These meats can contribute to elevated fat consumption, placing undue strain on the pancreas and increasing the susceptibility to pancreatic inflammation. Prioritizing lean cuts of meat and skinless poultry can help maintain a balanced fat intake and support pancreatic health.
-
Rich Dairy Products: Dairy products high in fat, such as full-fat cheese and creamy desserts, should be avoided for dogs at risk of pancreatitis. The high-fat content in these products can disrupt digestive function and potentially exacerbate pancreatic inflammation. Opting for low-fat or fat-free dairy alternatives can help minimize the risk of pancreatic stress while still providing essential nutrients.
-
Fried and Processed Foods: Fried foods and processed snacks laden with unhealthy fats should be omitted from the diet of dogs prone to pancreatitis. These foods can contribute to excessive fat consumption and metabolic strain, posing a heightened risk of pancreatic distress. Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods and opting for cooking methods such as baking or steaming can support digestive wellness and reduce the risk of pancreatitis.
-
Excessive Treats and Table Scraps: Indulging dogs prone to pancreatitis with excessive treats and table scraps can disrupt dietary balance and contribute to heightened fat intake. It is crucial to exercise moderation and select low-fat, pancreatitis-friendly treats to minimize the risk of digestive disturbances. Additionally, refraining from offering table scraps, especially those high in fat, can help maintain dietary equilibrium and support pancreatic health.
By being mindful of these dietary exclusions and prioritizing a balanced, low-fat diet, pet owners can play a pivotal role in preventing pancreatitis and promoting overall well-being in their dogs. Through proactive dietary management and a focus on pancreatitis-friendly foods, pet owners can empower themselves to support their dog's digestive health and mitigate the risk of pancreatic inflammation.
Read more: How To Stop Dog Anxiety Peeing
Tips for Feeding a Dog with a History of Pancreatitis
Feeding a dog with a history of pancreatitis requires a thoughtful and tailored approach to support their digestive health and overall well-being. By implementing specific strategies and dietary modifications, pet owners can navigate the nuances of feeding a dog with a history of pancreatitis, promoting optimal nutrition while mitigating the risk of pancreatic flare-ups.
1. Gradual Transition to New Diet
When transitioning a dog with a history of pancreatitis to a new diet, gradual and incremental changes are essential. Abrupt dietary shifts can disrupt digestive equilibrium and potentially trigger pancreatic distress. By slowly introducing the new diet and monitoring the dog's response, pet owners can minimize the likelihood of digestive disturbances and facilitate a smooth transition.
2. Small, Frequent Meals
Opting for small, frequent meals as opposed to large, infrequent feedings can alleviate the strain on the pancreas and support optimal digestion. By dividing the daily food portions into several smaller meals, pet owners can help prevent excessive stimulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion, promoting digestive comfort and minimizing the risk of pancreatitis recurrence.
3. Low-Fat, Digestible Foods
Prioritizing low-fat, easily digestible foods is paramount when feeding a dog with a history of pancreatitis. Selecting high-quality, lean protein sources and incorporating complex carbohydrates can help maintain a balanced and pancreatitis-friendly diet. Additionally, avoiding high-fat treats and table scraps is crucial to prevent undue stress on the pancreas.
4. Consultation with a Veterinarian
Seeking guidance from a veterinarian specializing in pet nutrition can provide invaluable insights into tailoring a diet suitable for a dog with a history of pancreatitis. A veterinarian can offer personalized recommendations, considering the dog's specific health status and dietary requirements, to optimize their nutritional intake and minimize the risk of pancreatic complications.
5. Monitoring and Observation
Regular monitoring of the dog's dietary response and overall well-being is essential for identifying any potential signs of digestive distress or pancreatitis recurrence. By staying vigilant and observant of changes in appetite, stool quality, and behavior, pet owners can promptly address any emerging concerns and adjust the diet as needed to support the dog's digestive health.
By adhering to these tips and implementing a customized feeding approach, pet owners can effectively manage the dietary needs of a dog with a history of pancreatitis. Through a combination of mindful dietary choices, portion control, and attentive monitoring, pet owners can play a proactive role in supporting their dog's digestive wellness and minimizing the risk of pancreatitis relapse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between diet and pancreatitis in dogs underscores the pivotal role of nutrition in safeguarding the pancreatic health of our beloved pets. By understanding the multifaceted nature of pancreatitis and its potential triggers, pet owners can proactively implement dietary strategies to mitigate the risk of this inflammatory condition. Prioritizing a balanced and wholesome diet that emphasizes lean protein sources, controlled fat intake, complex carbohydrates, and nutrient-dense foods forms the cornerstone of preventive measures against pancreatitis.
The recommended diet for dogs to prevent pancreatitis encompasses a thoughtful selection of foods that support digestive wellness while minimizing the potential burden on the pancreas. By prioritizing lean protein sources, moderate fat intake, and complex carbohydrates, pet owners can optimize their dog's nutritional intake to promote overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of pancreatic inflammation.
Furthermore, being mindful of foods to avoid for dogs prone to pancreatitis is essential in eliminating potential triggers that can exacerbate the risk of pancreatic inflammation. By steering clear of high-fat foods, fatty meats, rich dairy products, fried and processed foods, and excessive treats and table scraps, pet owners can proactively safeguard their dog's well-being and reduce the likelihood of pancreatitis flare-ups.
Feeding a dog with a history of pancreatitis requires a tailored approach, encompassing gradual dietary transitions, small and frequent meals, low-fat and digestible foods, consultation with a veterinarian, and vigilant monitoring. By adhering to these strategies, pet owners can effectively manage the dietary needs of their dogs, supporting digestive wellness and minimizing the risk of pancreatitis relapse.
In essence, the significance of a well-balanced diet in preventing pancreatitis cannot be overstated. By equipping pet owners with valuable insights into the impact of nutrition on pancreatic health, this guide aims to empower them to make informed dietary choices for their furry companions. Through a holistic approach to nutrition and proactive management, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their dog's digestive health and promoting overall vitality.