Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>When Are Fleas Most Active On Dogs


Common Health Issues
When Are Fleas Most Active On Dogs
Published: February 14, 2024
Learn about common health issues for dogs and find out when fleas are most active on dogs. Protect your pet from potential health risks.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Fleas are tiny, wingless parasites that thrive on the blood of mammals and birds. These pesky creatures are a common nuisance for dogs and their owners, causing discomfort and potential health issues. Understanding the factors that influence flea activity is crucial for effectively managing and preventing infestations.
Flea activity can vary depending on environmental conditions, seasonal changes, and the presence of suitable hosts. By gaining insight into the patterns of flea activity, dog owners can take proactive measures to protect their pets and homes from infestations.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of flea activity, explore the factors that influence their prevalence, and discuss the signs of flea infestation. Additionally, we will provide valuable insights into controlling flea activity, empowering dog owners with the knowledge to safeguard their beloved pets from these persistent pests.
Read more: Dog Yelps When Bitten By Fleas
Understanding Flea Activity
Flea activity refers to the periods when fleas are most active and prevalent in their environment, particularly on dogs. Understanding the dynamics of flea activity is essential for dog owners to effectively manage and prevent infestations. Fleas are most active during warm and humid conditions, typically thriving in temperatures ranging from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit and humidity levels of 70% or higher. These optimal environmental conditions provide an ideal habitat for fleas to reproduce and proliferate.
Flea activity is also influenced by the availability of hosts, such as dogs, cats, and other mammals. Fleas rely on these hosts for blood meals, and the presence of suitable hosts directly impacts their activity levels. When dogs spend time outdoors in areas where fleas are prevalent, such as grassy yards, parks, or wooded areas, they are at a higher risk of encountering fleas. Additionally, interactions with other infested animals can lead to the transfer of fleas onto dogs, further contributing to flea activity.
Understanding the life cycle of fleas is crucial in comprehending their activity patterns. Fleas undergo complete metamorphosis, progressing through four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The entire life cycle can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions. During the pupal stage, fleas can remain dormant for extended periods, waiting for favorable conditions to emerge as adults. This dormancy allows fleas to survive in the environment even when hosts are not present, contributing to ongoing flea activity.
Furthermore, flea activity can be influenced by seasonal changes. In temperate regions, flea populations tend to peak during the warmer months, particularly in late spring and summer. During these seasons, the combination of elevated temperatures and increased outdoor activities for dogs creates an environment conducive to heightened flea activity. However, in regions with milder climates, fleas can remain active throughout the year, posing a persistent threat to dogs and their owners.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of flea activity, dog owners can proactively implement preventive measures to protect their pets. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions regarding flea control and management, ultimately ensuring the well-being of their beloved canine companions.
Factors Affecting Flea Activity
Several factors play a pivotal role in influencing flea activity, ultimately impacting the prevalence and persistence of infestations. Understanding these factors is essential for dog owners to effectively manage and mitigate the risks associated with fleas.
-
Environmental Conditions: Flea activity is significantly influenced by environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Fleas thrive in warm and humid environments, with optimal activity occurring at temperatures ranging from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit and humidity levels of 70% or higher. These conditions provide an ideal habitat for fleas to reproduce and proliferate, contributing to heightened flea activity.
-
Host Availability: The presence of suitable hosts, including dogs, cats, and other mammals, directly impacts flea activity. Fleas rely on these hosts for blood meals, and the availability of potential hosts influences their activity levels. When dogs spend time in outdoor environments where fleas are prevalent, such as grassy yards, parks, or wooded areas, they are at an increased risk of encountering fleas. Interactions with other infested animals can also lead to the transfer of fleas onto dogs, further contributing to flea activity.
-
Life Cycle Dynamics: Understanding the life cycle of fleas is crucial in comprehending their activity patterns. Fleas undergo complete metamorphosis, progressing through four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The duration of the life cycle is influenced by environmental conditions, with optimal temperatures and humidity levels accelerating the development of fleas. Additionally, the pupal stage allows fleas to remain dormant for extended periods, contributing to ongoing flea activity even in the absence of hosts.
-
Seasonal Variations: Flea activity is also influenced by seasonal changes. In temperate regions, flea populations tend to peak during the warmer months, particularly in late spring and summer. During these seasons, the combination of elevated temperatures and increased outdoor activities for dogs creates an environment conducive to heightened flea activity. However, in regions with milder climates, fleas can remain active throughout the year, posing a persistent threat to dogs and their owners.
By considering these factors, dog owners can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of flea activity, enabling them to implement proactive measures to protect their pets. Awareness of environmental conditions, host interactions, life cycle dynamics, and seasonal variations empowers dog owners to make informed decisions regarding flea control and management, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of their beloved canine companions.
Signs of Flea Infestation
Identifying the signs of flea infestation is crucial for dog owners to promptly address and mitigate the impact of these persistent parasites. Recognizing the indicators of flea presence enables proactive measures to be taken, safeguarding the well-being of dogs and preventing the escalation of infestations.
-
Excessive Scratching and Biting: Dogs affected by fleas often exhibit increased scratching and biting behavior. Persistent scratching, particularly around the neck, ears, and base of the tail, may indicate the presence of fleas. Additionally, dogs may excessively chew or lick their fur in response to flea bites, leading to skin irritation and potential hair loss.
-
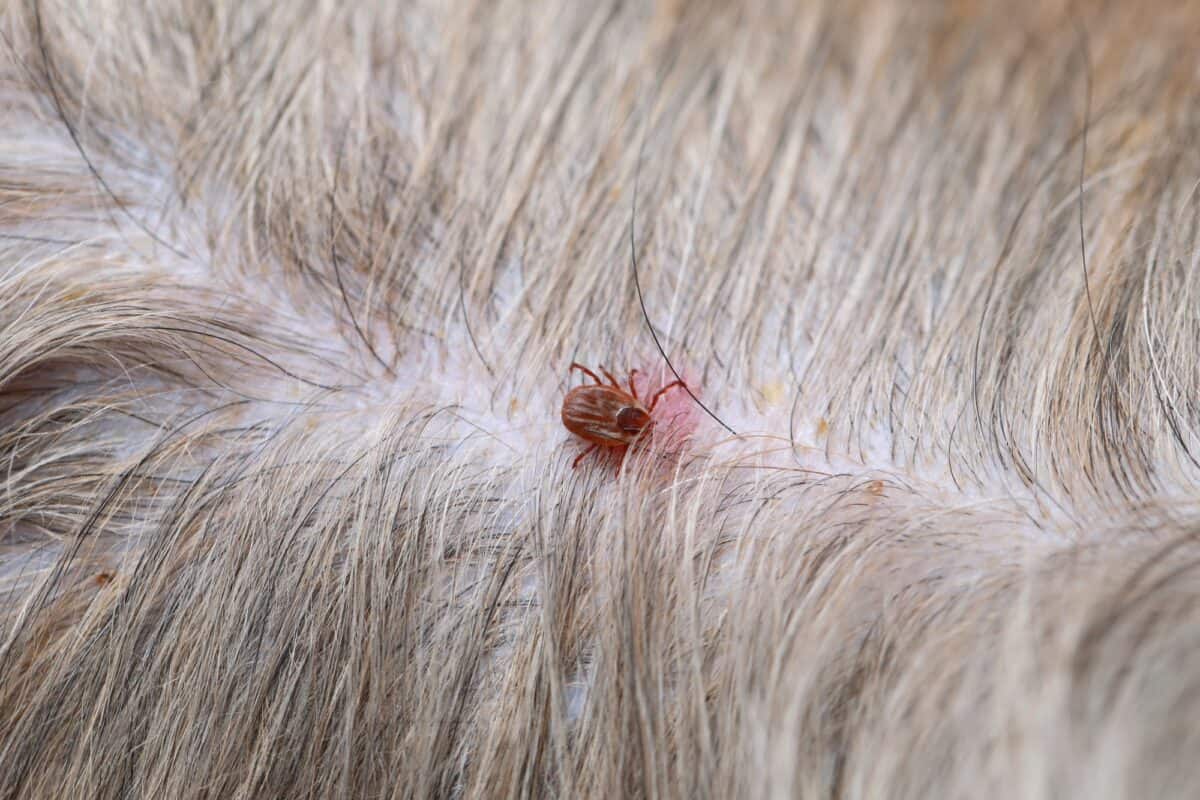
Visible Fleas or Flea Dirt: Flea dirt, which appears as tiny black specks resembling ground pepper, is a telltale sign of flea infestation. This excrement consists of digested blood excreted by fleas and is commonly found on the dog's skin and fur. In severe infestations, live fleas may also be visible on the dog's coat, especially in areas with dense fur.
-
Skin Irritation and Redness: Flea bites can cause allergic reactions in dogs, resulting in skin irritation, redness, and the formation of small, raised bumps. Dogs may experience discomfort and exhibit signs of agitation due to the itching and discomfort caused by flea bites.
-
Restlessness and Agitation: Infested dogs may display restlessness and agitation, often accompanied by difficulty in settling down or finding a comfortable resting position. Flea bites can cause discomfort and distress, leading to behavioral changes in affected dogs.
-
Hair Loss and Hot Spots: Prolonged flea infestations can lead to hair loss, particularly in areas where dogs excessively scratch or bite to alleviate itching. Additionally, hot spots, characterized by inflamed and moist skin lesions, may develop as a result of flea bites and subsequent skin irritation.
-
Anemia and Weakness: In severe cases of flea infestation, particularly in young or small dogs, the loss of blood due to continuous flea feeding can lead to anemia. Dogs may exhibit weakness, lethargy, and pale gums, indicating the detrimental impact of prolonged flea infestations on their health.
By recognizing these signs of flea infestation, dog owners can take proactive steps to address the issue effectively. Implementing regular flea prevention measures, such as topical treatments, oral medications, and environmental control, is essential for managing flea infestations and ensuring the well-being of dogs. Additionally, consulting a veterinarian for guidance on flea control and treatment options can aid in mitigating the impact of flea infestations on canine companions.
Controlling Flea Activity
Controlling flea activity is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of dogs and preventing the escalation of infestations. By implementing comprehensive flea control measures, dog owners can effectively manage and mitigate the risks associated with fleas, creating a safe and comfortable environment for their beloved pets.
Read more: Can My Dog Get Fleas When On Trifexis?
1. Regular Flea Prevention:
Implementing a proactive approach to flea prevention is crucial for controlling flea activity. Utilizing veterinarian-recommended flea prevention products, such as topical treatments, oral medications, and flea collars, can significantly reduce the risk of infestations. Regular application of these preventive measures helps to repel and eliminate fleas, safeguarding dogs from potential infestations.
2. Environmental Control:
Maintaining a clean and flea-free environment is paramount in controlling flea activity. Regular vacuuming of carpets, rugs, and upholstery, along with washing pet bedding and linens in hot water, helps to eliminate flea eggs, larvae, and pupae from the environment. Additionally, outdoor areas frequented by dogs should be kept tidy, with grass trimmed and debris removed to minimize flea habitats.
3. Pet Grooming and Hygiene:
Regular grooming and hygiene practices for dogs play a pivotal role in controlling flea activity. Bathing dogs with flea-repellent shampoos and utilizing flea combs can help remove adult fleas and their eggs from the coat. Maintaining a well-groomed and clean coat reduces the likelihood of flea infestations, contributing to effective flea control.
4. Integrated Pest Management:
Adopting an integrated pest management approach involves utilizing multiple strategies to control flea activity. This may include the use of natural remedies, such as diatomaceous earth, to dehydrate and eliminate fleas in the environment. Additionally, seeking professional pest control services for targeted treatment of indoor and outdoor areas can aid in comprehensive flea management.
Read more: What To Do When Your Dog Has Fleas
5. Consultation with Veterinarian:
Seeking guidance from a veterinarian is essential for developing a tailored flea control plan based on the specific needs of dogs. Veterinarians can recommend suitable flea prevention products, provide insights into environmental control measures, and offer guidance on addressing existing flea infestations. Regular check-ups and consultations with veterinarians contribute to proactive flea control and management.
By incorporating these comprehensive flea control measures into their routine, dog owners can effectively manage and mitigate flea activity, ensuring the well-being and comfort of their canine companions. Proactive flea control not only protects dogs from the discomfort and health risks associated with fleas but also creates a harmonious living environment for both pets and their owners.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of flea activity and the factors influencing their prevalence is paramount for dog owners seeking to protect their beloved pets from infestations. Fleas are most active during warm and humid conditions, thriving in temperatures ranging from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit and humidity levels of 70% or higher. The availability of suitable hosts, the life cycle dynamics of fleas, and seasonal variations further contribute to their activity levels.
Recognizing the signs of flea infestation, including excessive scratching, visible fleas or flea dirt, skin irritation, restlessness, and potential health implications, is crucial for prompt intervention. By identifying these indicators, dog owners can take proactive measures to address and mitigate the impact of fleas on their pets.
Controlling flea activity involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing regular flea prevention, environmental control, pet grooming and hygiene, integrated pest management, and consultation with veterinarians. By implementing these comprehensive flea control measures, dog owners can effectively manage and mitigate the risks associated with fleas, creating a safe and comfortable environment for their beloved pets.
Ultimately, proactive flea control not only protects dogs from the discomfort and health risks associated with fleas but also fosters a harmonious living environment for both pets and their owners. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of flea activity and diligently implementing preventive measures, dog owners can ensure the well-being and happiness of their canine companions, fostering a thriving and flea-free environment for all.