Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Muscular and Joint Health>What Can You Do For A Dog That Has Arthritis In Its Legs


Muscular and Joint Health
What Can You Do For A Dog That Has Arthritis In Its Legs
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover effective solutions for improving your dog's muscular and joint health, including tips for managing arthritis in its legs. Explore expert advice and products to support your pet's mobility and well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Arthritis is a common condition that affects not only humans but also our beloved canine companions. Just like in humans, arthritis in dogs can cause discomfort, pain, and decreased mobility. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to understand the impact of arthritis on our furry friends and explore the various ways to alleviate their discomfort and improve their quality of life.
Dogs are known for their boundless energy and enthusiasm, but when arthritis sets in, it can significantly diminish their zest for life. Whether it's osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other forms of joint inflammation, the effects can be debilitating for our four-legged friends. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for canine arthritis is essential for providing the best possible care for our furry companions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of arthritis in dogs, shedding light on the signs and symptoms, treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary considerations that can make a meaningful difference in the lives of arthritic dogs. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition and the available interventions, pet owners can take proactive steps to support their dogs' joint health and overall well-being.
As we embark on this journey to explore the realm of canine arthritis, it's important to approach the topic with empathy and a genuine desire to enhance the lives of our loyal canine companions. Together, let's unravel the complexities of arthritis in dogs and discover the myriad ways to provide comfort, relief, and joy to our furry friends who rely on us for love and care.
Understanding Arthritis in Dogs
Arthritis, a term derived from the Greek words "arthro," meaning joint, and "itis," denoting inflammation, is a condition characterized by inflammation and stiffness in the joints. When this condition affects dogs, it can significantly impact their mobility and overall quality of life. Canine arthritis can manifest in various forms, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and infectious arthritis, each with its unique causes and characteristics.
Osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis in dogs, typically develops as a result of wear and tear on the joints over time. This wear and tear can be attributed to factors such as aging, genetics, obesity, joint instability, or previous joint injuries. As the protective cartilage within the joints deteriorates, the bones may begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility for the affected dog.
Rheumatoid arthritis, although less common in dogs than in humans, is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, including the joints. This can result in chronic inflammation, joint damage, and discomfort for the affected dog.
Infectious arthritis, also known as septic arthritis, is caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection that enters the joint, triggering inflammation and potentially causing irreversible damage to the joint tissues. This form of arthritis in dogs often requires prompt and targeted treatment to address the underlying infection and alleviate the associated joint symptoms.
Understanding the specific type of arthritis affecting a dog is crucial for devising an effective treatment plan and providing targeted support. By recognizing the distinct characteristics and underlying causes of arthritis in dogs, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to implement tailored interventions that address the unique needs of each affected dog.
As we continue to explore the multifaceted nature of arthritis in dogs, it becomes evident that this condition demands careful attention, empathy, and a proactive approach to mitigate its impact on our canine companions. By deepening our understanding of the complexities of arthritis in dogs, we can pave the way for informed decision-making and compassionate care that enhances the well-being of our furry friends.
Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis in Dogs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of arthritis in dogs is pivotal for early intervention and effective management of this condition. While dogs are adept at masking discomfort, several subtle cues can indicate the presence of arthritis. Observant pet owners can look out for the following indicators that may point to arthritis in their canine companions:
-
Limping or Favoring Certain Limbs: Dogs with arthritis may exhibit a noticeable limp or favor specific limbs, especially after periods of rest or physical activity. This reluctance to put weight on a particular leg can signal joint discomfort and stiffness.
-
Decreased Activity and Reluctance to Exercise: Arthritic dogs may display a reduced interest in physical activities they once enjoyed. Reluctance to engage in play, exercise, or walks can be indicative of joint pain and discomfort.
-
Stiffness and Difficulty Rising: Dogs with arthritis may experience stiffness, particularly after prolonged periods of inactivity. They may struggle to rise from a lying or sitting position, and their movements may appear hesitant or labored.
-
Licking or Chewing at Joints: Persistent licking or chewing at specific joints can be a sign of discomfort or irritation. Dogs may instinctively target the affected joints in an attempt to alleviate pain or discomfort.
-
Behavioral Changes: Arthritic dogs may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased irritability, restlessness, or a preference for solitude. These shifts in demeanor can stem from the physical discomfort and emotional distress associated with arthritis.
-
Muscle Atrophy and Joint Deformities: Over time, arthritis can lead to muscle atrophy and visible joint deformities in affected dogs. These physical changes may become apparent as the condition progresses.
-
Audible Signs of Pain: Dogs with arthritis may vocalize their discomfort through whining, whimpering, or groaning, especially when attempting to move or when pressure is applied to the affected joints.
By remaining attuned to these subtle yet telling signs, pet owners can promptly seek veterinary evaluation and implement appropriate measures to alleviate their dogs' discomfort. Early recognition of arthritis symptoms enables proactive intervention, fostering improved joint health and enhanced quality of life for arthritic dogs.
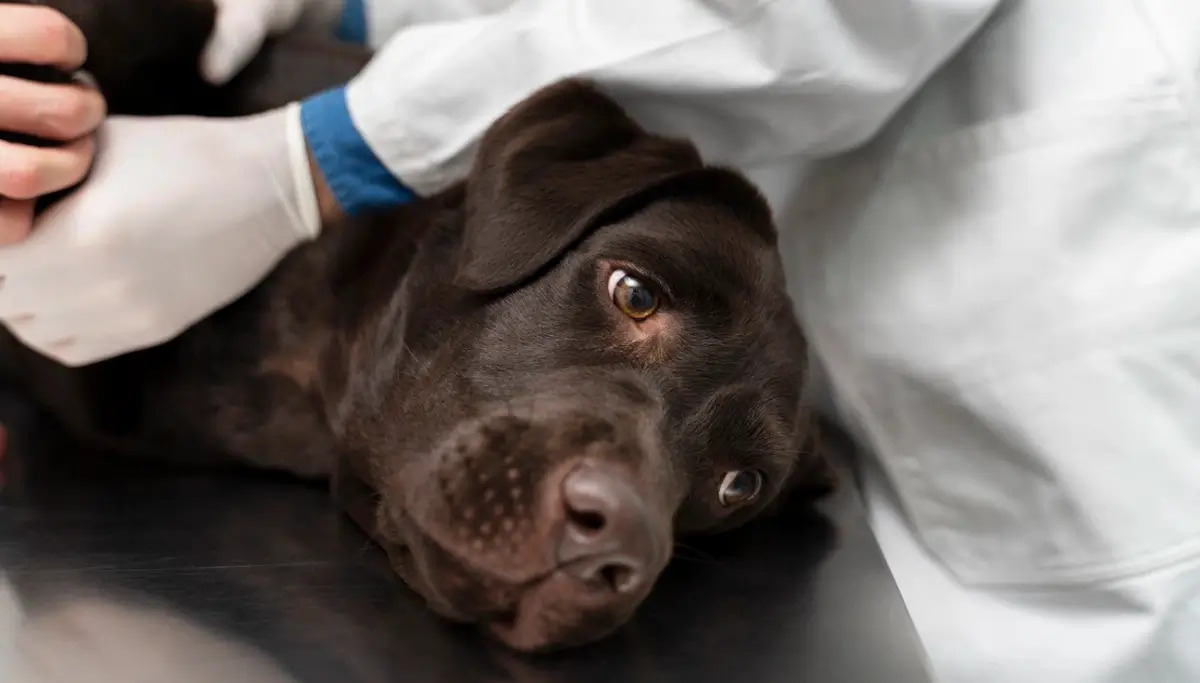
Consulting with a Veterinarian
When a dog exhibits signs of arthritis, consulting with a veterinarian is the crucial first step toward understanding the extent of the condition and formulating an effective treatment plan. Veterinarians possess the expertise and diagnostic tools necessary to assess the severity of arthritis in dogs and recommend tailored interventions to alleviate discomfort and enhance mobility.
During the veterinary consultation, the veterinarian will conduct a comprehensive physical examination of the dog, focusing on the affected joints and observing the dog's gait, range of motion, and overall mobility. This examination may involve gentle manipulation of the joints to assess pain, swelling, and stiffness. Additionally, the veterinarian may inquire about the dog's medical history, previous injuries, and any changes in behavior or activity levels that the pet owner has observed.
In some cases, the veterinarian may recommend diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays or joint fluid analysis, to obtain a detailed view of the affected joints and confirm the presence of arthritis. These diagnostic tools can reveal the extent of joint damage, the presence of bone spurs, and the degree of cartilage deterioration, providing valuable insights into the progression of the condition.
Based on the findings from the physical examination and diagnostic tests, the veterinarian will collaborate with the pet owner to develop a customized treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of the arthritic dog. This plan may encompass various modalities, including medication to manage pain and inflammation, dietary adjustments to support joint health, and lifestyle modifications to accommodate the dog's mobility limitations.
Furthermore, the veterinarian can offer guidance on appropriate exercise regimens, physical therapy techniques, and supportive measures to enhance the dog's comfort and overall well-being. By leveraging the veterinarian's expertise and personalized recommendations, pet owners can gain valuable insights into the most effective strategies for managing their dog's arthritis and promoting joint health.
In essence, consulting with a veterinarian empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog's arthritis care, ensuring that the interventions implemented are tailored to the dog's unique needs and aligned with the overarching goal of enhancing the dog's quality of life. Through open communication and collaborative partnership with the veterinarian, pet owners can navigate the complexities of arthritis in dogs with confidence and compassion, fostering a supportive environment that prioritizes the well-being of their beloved canine companions.
Treatment Options for Arthritic Dogs
Addressing arthritis in dogs necessitates a multifaceted approach that encompasses various treatment modalities aimed at mitigating pain, reducing inflammation, and enhancing joint function. When formulating a comprehensive treatment plan for arthritic dogs, veterinarians may recommend the following interventions:
-
Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with arthritis in dogs. These medications help manage discomfort and improve the dog's mobility. Additionally, veterinarians may recommend joint supplements containing glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids to support joint health and reduce cartilage degeneration.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy techniques, including massage, hydrotherapy, and low-impact exercises, can play a pivotal role in maintaining the dog's muscle strength, enhancing flexibility, and promoting overall joint function. These therapeutic interventions are tailored to the specific needs and limitations of arthritic dogs, aiming to improve their mobility and quality of life.
-
Weight Management: Obesity exacerbates the strain on arthritic joints, leading to increased discomfort and reduced mobility. Therefore, implementing a balanced diet and weight management plan is essential for arthritic dogs. By maintaining a healthy weight, the stress on the joints is minimized, contributing to enhanced joint function and reduced pain.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Adapting the dog's living environment to accommodate their mobility limitations is crucial. This may involve providing supportive bedding, ramps or steps to facilitate movement, and minimizing activities that exacerbate joint strain. Creating a comfortable and accessible living space can significantly enhance the well-being of arthritic dogs.
-
Acupuncture and Laser Therapy: Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and low-level laser therapy have shown promise in alleviating pain and inflammation in arthritic dogs. These non-invasive modalities can complement traditional treatments, offering additional avenues for managing arthritis-related discomfort.
-
Surgical Interventions: In severe cases of arthritis, surgical options such as joint replacement or arthroscopic procedures may be considered to address advanced joint damage and restore mobility. These interventions are typically recommended when conservative treatments have proven insufficient in managing the dog's arthritis symptoms.
By integrating these diverse treatment options, veterinarians strive to create tailored care plans that address the unique needs of arthritic dogs, aiming to alleviate discomfort, enhance mobility, and improve their overall quality of life. Each intervention is carefully selected and customized to align with the specific requirements of the individual dog, ensuring that the treatment approach is comprehensive, effective, and conducive to long-term joint health.
In essence, the treatment options for arthritic dogs are designed to provide holistic support, encompassing pharmaceutical, rehabilitative, and lifestyle-based interventions that collectively contribute to the well-being of dogs grappling with arthritis. Through a concerted effort to implement these diverse treatment modalities, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to optimize the care and comfort of arthritic dogs, fostering a nurturing environment that prioritizes their joint health and overall vitality.
Lifestyle Changes to Help Arthritic Dogs
Implementing lifestyle changes tailored to the unique needs of arthritic dogs is instrumental in fostering a supportive environment that promotes their comfort, mobility, and overall well-being. By incorporating thoughtful adjustments to the dog's daily routine and living space, pet owners can significantly enhance the quality of life for their canine companions grappling with arthritis.
Supportive Bedding and Rest Areas
Providing arthritic dogs with supportive and orthopedic bedding can alleviate pressure on their joints and enhance their overall comfort. Orthopedic dog beds are designed to distribute the dog's weight evenly, reducing strain on arthritic joints and facilitating restful sleep. Additionally, placing these beds in warm and draft-free areas can further enhance the dog's relaxation and joint mobility.
Accessible Living Spaces
Adapting the dog's living environment to accommodate their mobility limitations is essential. Installing ramps or steps to facilitate access to elevated surfaces, such as sofas or beds, can minimize the strain on arthritic joints when the dog moves around the house. Moreover, ensuring that food and water bowls are easily accessible at a comfortable height can reduce the need for strenuous bending or stretching, promoting the dog's ease of movement.
Controlled Exercise and Play
While regular exercise is crucial for maintaining the overall health of dogs, it's important to modify the intensity and duration of physical activities for arthritic dogs. Low-impact exercises, such as gentle walks and swimming, can help maintain muscle strength and joint flexibility without placing excessive stress on the affected joints. Engaging in controlled play sessions that avoid abrupt movements or high-impact activities can further safeguard the dog's joint health while allowing them to enjoy physical stimulation.
Read more: What To Do If A Dog Has Fleas In Its Ear
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount for arthritic dogs, as excess body weight exacerbates joint strain and discomfort. By working closely with the veterinarian to develop a balanced diet and portion control plan, pet owners can help their dogs achieve and maintain an optimal weight. This proactive approach to weight management can significantly alleviate the burden on arthritic joints, contributing to improved mobility and reduced pain.
Warmth and Comfort
Ensuring that arthritic dogs are kept warm and comfortable is essential for managing their joint stiffness and discomfort. During colder months, providing cozy blankets and ensuring that the living space is adequately heated can help soothe the dog's joints and alleviate stiffness. Additionally, gentle massages and warm compresses can offer therapeutic relief, promoting relaxation and enhancing the dog's overall well-being.
By embracing these lifestyle changes and creating a nurturing environment that caters to the specific needs of arthritic dogs, pet owners can play a pivotal role in enhancing their canine companions' comfort and mobility. These thoughtful adjustments, when integrated into the dog's daily routine and living space, contribute to a supportive and enriching environment that prioritizes the joint health and overall vitality of arthritic dogs.
Exercise and Physical Therapy for Arthritic Dogs
Exercise and physical therapy play a pivotal role in managing arthritis in dogs, aiming to maintain muscle strength, enhance joint flexibility, and promote overall mobility while minimizing discomfort. Tailoring exercise regimens and therapeutic interventions to the specific needs and limitations of arthritic dogs is essential for fostering their well-being and quality of life.
Low-impact exercises, such as leisurely walks and swimming, offer valuable opportunities for arthritic dogs to engage in physical activity without placing excessive strain on their joints. These activities help sustain muscle tone, improve circulation, and support joint flexibility, contributing to the dog's overall joint health. By incorporating controlled and gentle exercise sessions into the dog's routine, pet owners can facilitate physical stimulation while safeguarding the dog from undue discomfort.
Physical therapy techniques, including massage, hydrotherapy, and range-of-motion exercises, are instrumental in addressing the unique challenges posed by arthritis in dogs. Massage therapy can alleviate muscle tension, enhance circulation, and provide soothing relief to arthritic joints. Hydrotherapy, which involves controlled swimming or walking in water, offers a low-impact yet effective means of improving muscle strength and joint mobility. Additionally, range-of-motion exercises can help maintain joint flexibility and prevent stiffness, empowering arthritic dogs to move with greater ease and comfort.
Furthermore, incorporating supportive measures such as warm compresses and gentle stretching into the dog's physical therapy regimen can offer therapeutic benefits, promoting relaxation and enhancing the dog's overall well-being. These interventions are tailored to the specific needs of arthritic dogs, aiming to mitigate discomfort, enhance mobility, and foster a nurturing environment that prioritizes their joint health.
By integrating exercise and physical therapy into the care plan for arthritic dogs, pet owners can actively contribute to the dog's joint health and overall vitality. These proactive measures, when implemented with empathy and attentiveness, can significantly enhance the comfort and quality of life for dogs grappling with arthritis, underscoring the profound impact of tailored exercise and therapeutic interventions in supporting their well-being.
Dietary Considerations for Arthritic Dogs
Dietary considerations play a pivotal role in managing arthritis in dogs, offering a proactive avenue for supporting joint health, managing inflammation, and promoting overall well-being. Tailoring the dog's diet to address the specific nutritional needs associated with arthritis can significantly contribute to alleviating discomfort and enhancing mobility.
Incorporating joint-friendly nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, and chondroitin into the dog's diet can offer valuable support for arthritic joints. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint inflammation and alleviate pain in arthritic dogs. Additionally, glucosamine and chondroitin, often included in specialized joint supplements or found in natural food sources, support cartilage health and may aid in slowing the progression of joint degeneration.
Opting for a balanced and nutrient-rich diet that includes high-quality protein sources, essential fatty acids, and a variety of vitamins and minerals is essential for supporting the overall health of arthritic dogs. Lean proteins, such as chicken, turkey, and fish, provide essential amino acids that contribute to muscle maintenance and overall vitality. Furthermore, incorporating a diverse array of fruits and vegetables, such as blueberries, spinach, and sweet potatoes, can supply valuable antioxidants and phytonutrients that support the dog's immune system and overall health.
Weight management is a critical aspect of dietary considerations for arthritic dogs, as excess body weight places added strain on the joints, exacerbating discomfort and reducing mobility. Working closely with the veterinarian to determine the ideal weight for the dog and implementing portion control and a balanced diet can help manage the dog's weight effectively, contributing to improved joint function and reduced pain.
Moreover, ensuring that the dog remains adequately hydrated is essential for supporting joint health and overall well-being. Providing access to fresh, clean water at all times is crucial, as proper hydration supports joint lubrication and facilitates the body's natural healing processes.
By embracing these dietary considerations and tailoring the dog's nutrition to address the specific needs associated with arthritis, pet owners can actively contribute to the dog's joint health and overall vitality. These proactive measures, when integrated into the dog's daily diet, offer a holistic approach to managing arthritis, underscoring the profound impact of nutrition in supporting the well-being of arthritic dogs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey through the realm of arthritis in dogs has provided valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of this condition and the myriad ways to support the joint health and overall well-being of our beloved canine companions. By delving into the understanding of arthritis in dogs, recognizing its signs and symptoms, consulting with veterinarians, exploring treatment options, implementing lifestyle changes, embracing exercise and physical therapy, and considering dietary considerations, pet owners can proactively navigate the complexities of arthritis and provide compassionate care that enhances the lives of arthritic dogs.
Arthritis, whether osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or infectious arthritis, can significantly impact a dog's mobility and quality of life. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, such as limping, decreased activity, stiffness, and muscle atrophy, empowers pet owners to seek timely veterinary evaluation and implement tailored interventions to alleviate their dogs' discomfort.
Consulting with a veterinarian is pivotal in understanding the extent of the condition and formulating an effective treatment plan. Through open communication and collaborative partnership with the veterinarian, pet owners can navigate the complexities of arthritis in dogs with confidence and compassion, fostering a supportive environment that prioritizes the well-being of their beloved canine companions.
The treatment options for arthritic dogs encompass diverse modalities, including medication, physical therapy, weight management, lifestyle modifications, and surgical interventions, all aimed at mitigating pain, reducing inflammation, and enhancing joint function. By integrating these interventions, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to optimize the care and comfort of arthritic dogs, fostering a nurturing environment that prioritizes their joint health and overall vitality.
Lifestyle changes tailored to the unique needs of arthritic dogs, such as providing supportive bedding, creating accessible living spaces, and implementing controlled exercise and play, contribute to a supportive and enriching environment that prioritizes the joint health and overall vitality of arthritic dogs.
Exercise and physical therapy play a pivotal role in managing arthritis in dogs, aiming to maintain muscle strength, enhance joint flexibility, and promote overall mobility while minimizing discomfort. These proactive measures, when implemented with empathy and attentiveness, can significantly enhance the comfort and quality of life for dogs grappling with arthritis, underscoring the profound impact of tailored exercise and therapeutic interventions in supporting their well-being.
Dietary considerations tailored to address the specific nutritional needs associated with arthritis can significantly contribute to alleviating discomfort and enhancing mobility in arthritic dogs. By embracing these dietary considerations and tailoring the dog's nutrition, pet owners can actively contribute to the dog's joint health and overall vitality, offering a holistic approach to managing arthritis.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of arthritis in dogs and the proactive interventions explored in this guide underscore the profound impact of compassionate care and informed decision-making in enhancing the lives of arthritic dogs. By embracing empathy, attentiveness, and a commitment to proactive support, pet owners can navigate the complexities of arthritis with dedication and compassion, fostering an environment that prioritizes the joint health and overall well-being of their loyal canine companions.