Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How To Get An Embedded Tick Out Of A Dog

Common Health Issues
How To Get An Embedded Tick Out Of A Dog
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how to safely remove an embedded tick from your dog and prevent common health issues with our expert tips and guidance. Keep your furry friend healthy and happy!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
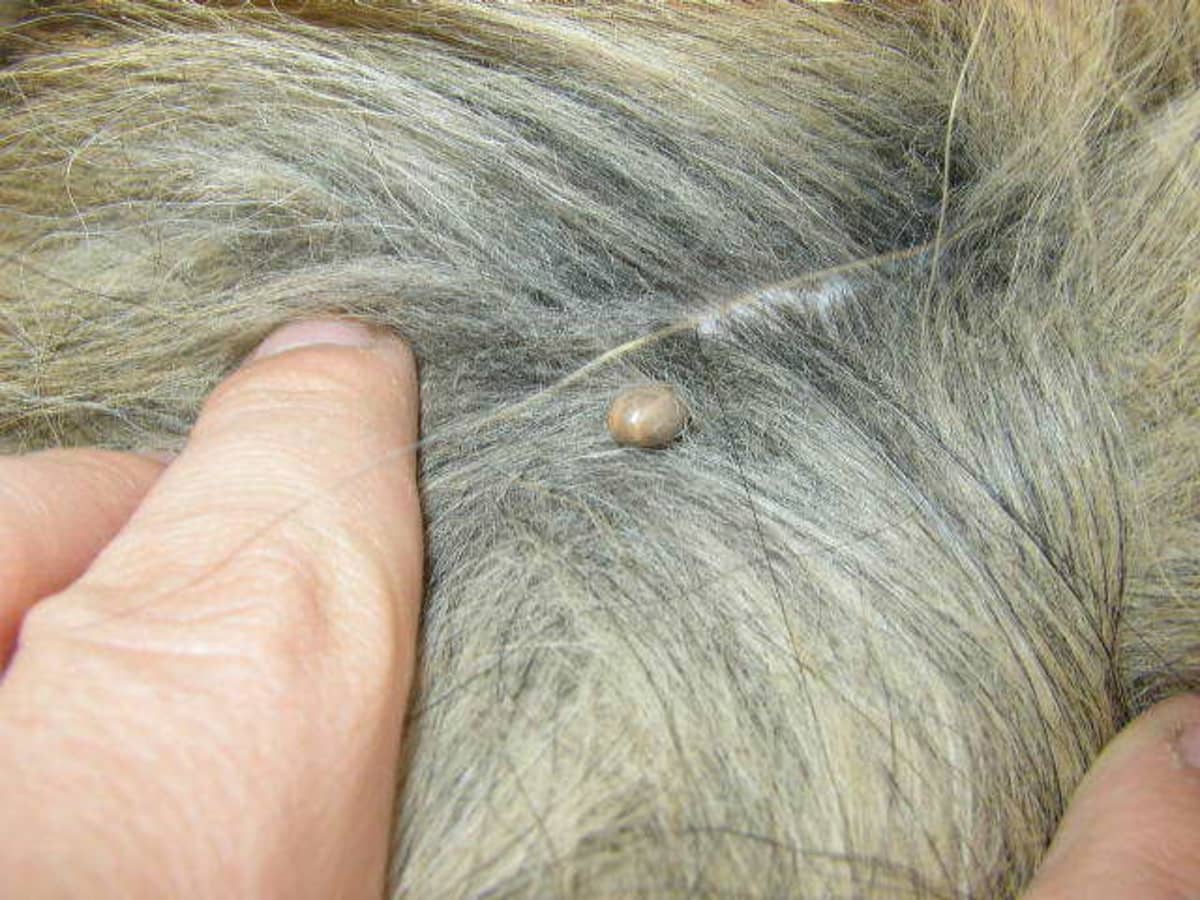
Ticks are pesky parasites that can pose serious health risks to dogs. These blood-sucking arachnids are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, and they latch onto dogs to feed on their blood. While the presence of a tick on a dog's skin is concerning, the real danger lies in the potential transmission of diseases such as Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis, and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
As a responsible pet owner, it's crucial to be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to safely remove an embedded tick from your dog. Prompt and proper tick removal can significantly reduce the risk of disease transmission and prevent potential complications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essential steps for safely removing an embedded tick from your dog. From understanding the risks associated with embedded ticks to providing aftercare and monitoring for tick-related illnesses, we will cover everything you need to know to protect your furry companion's well-being.
By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that you are well-prepared to handle the situation should you discover an embedded tick on your dog. Remember, proactive and informed care is key to safeguarding your dog's health and happiness.
Understanding the risks of embedded ticks
Ticks are more than just a nuisance for dogs; they can also transmit a variety of harmful diseases. When a tick becomes embedded in a dog's skin, it can transmit pathogens that lead to serious health issues. Understanding the risks associated with embedded ticks is crucial for pet owners to recognize the importance of prompt and proper tick removal.
One of the most common tick-borne illnesses is Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. If left untreated, Lyme disease can result in joint pain, lameness, and even kidney damage in dogs. Another concerning disease is ehrlichiosis, which is caused by the Ehrlichia bacteria transmitted through the bite of an infected tick. This condition can lead to fever, lethargy, and in severe cases, bleeding disorders. Anaplasmosis, caused by the Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacterium, can cause joint pain, fever, and lethargy in affected dogs. Additionally, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, transmitted by the American dog tick and the Rocky Mountain wood tick, can lead to fever, joint pain, and potentially fatal complications if not promptly addressed.
Beyond these specific diseases, the act of tick feeding itself can cause localized irritation and discomfort for the dog. Furthermore, some dogs may develop allergic reactions to tick saliva, leading to dermatitis and itching at the bite site.
It's important to note that the risk of disease transmission increases the longer a tick remains attached to a dog's skin. As such, swift and proper removal of embedded ticks is essential to minimize the likelihood of disease transmission and prevent potential health complications for the dog.
By understanding the potential risks associated with embedded ticks, pet owners can appreciate the urgency of addressing this issue promptly and effectively. With this awareness, they can take proactive measures to protect their dogs from the dangers posed by these blood-sucking parasites.
Tools and supplies needed for tick removal
When it comes to safely removing an embedded tick from a dog, having the right tools and supplies at your disposal is essential. Here's a comprehensive list of items you'll need to effectively and safely remove a tick from your furry friend:
1. Fine-tipped tweezers:
Fine-tipped tweezers are a crucial tool for tick removal. The fine tips allow for precise gripping of the tick's mouthparts, minimizing the risk of leaving any behind in the dog's skin. It's important to use tweezers specifically designed for tick removal to ensure proper handling.
2. Latex or nitrile gloves:
Wearing gloves during the tick removal process helps protect both you and your dog. Gloves serve as a barrier, reducing the risk of direct contact with the tick and potential pathogens it may carry. Additionally, gloves can prevent the transfer of any tick-borne diseases from the dog to the handler.
3. Rubbing alcohol or antiseptic wipes:
Before and after the tick removal procedure, it's essential to disinfect the area where the tick was embedded. Rubbing alcohol or antiseptic wipes can be used to clean the site, reducing the risk of infection and promoting proper wound care.
4. A small container or jar:
Having a small container or jar on hand is useful for safely storing the removed tick. This allows you to keep the tick for identification purposes in case your dog develops any symptoms of tick-borne illness. Additionally, storing the tick can be helpful if you need to consult a veterinarian regarding potential disease transmission.
5. Magnifying glass (optional):
While not essential, a magnifying glass can be helpful for examining the tick after removal. This can aid in identifying the species of tick and assessing its engorgement level, which may provide valuable information for evaluating the potential risk of disease transmission.
6. Tick removal tool (optional):
Some pet owners prefer using specialized tick removal tools, such as tick hooks or tick twisters. These tools are designed to grasp the tick at the skin's surface and facilitate safe removal. While not necessary, these devices can be beneficial for those who are uncomfortable using tweezers or dealing with particularly engorged ticks.
By ensuring that you have these essential tools and supplies readily available, you can approach the task of tick removal with confidence and preparedness. With the right equipment at your disposal, you can effectively and safely remove embedded ticks from your dog, minimizing the risk of disease transmission and promoting your pet's well-being.
Step-by-step guide to safely remove an embedded tick from a dog
-
Prepare the Area: Begin by selecting a well-lit and comfortable area for the tick removal process. It's essential to minimize distractions and ensure that both you and your dog are at ease. If your dog is particularly anxious, consider enlisting the help of another person to gently hold and soothe the dog during the procedure.
-
Put on Gloves: Prior to commencing the tick removal, don latex or nitrile gloves to protect yourself from direct contact with the tick and potential pathogens it may carry. This simple precaution can safeguard both you and your dog throughout the process.
-
Grasp the Tick: Using fine-tipped tweezers, carefully grasp the tick as close to the dog's skin as possible. Be gentle but firm, avoiding any sudden or jerky movements that could cause the tick to break apart. It's crucial to ensure that the tweezers are positioned near the tick's mouthparts to facilitate complete removal.
-
Remove the Tick: With a steady hand, steadily pull the tick straight out, exerting a gentle and even pressure. Avoid twisting or jerking motions, as these can cause the tick's mouthparts to break off and remain embedded in the dog's skin. The goal is to extract the tick intact, minimizing the risk of leaving any part behind.
-
Disinfect the Area: After successfully removing the tick, disinfect the bite site using rubbing alcohol or antiseptic wipes. Thoroughly clean the area to reduce the risk of infection and promote proper wound care. This step is crucial for ensuring the dog's comfort and well-being post-removal.
-
Dispose of the Tick: Place the removed tick in a small container or jar for safekeeping. This allows you to retain the tick for identification purposes and potential consultation with a veterinarian. Properly disposing of the tick ensures that it cannot reattach to the dog or pose a risk to other pets.
-
Monitor the Dog: Following the tick removal, closely monitor the dog for any signs of discomfort, redness, or inflammation at the bite site. Additionally, observe the dog for symptoms of tick-borne illnesses, such as fever, lethargy, or loss of appetite. Promptly consult a veterinarian if any concerning symptoms arise.
By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can effectively and safely remove an embedded tick from your dog, minimizing the risk of disease transmission and promoting your pet's well-being. Remember, patience, precision, and attentiveness are key to ensuring a successful tick removal process and safeguarding your dog's health.
Aftercare and monitoring for tick-related illnesses
After successfully removing an embedded tick from your dog, providing proper aftercare and vigilant monitoring is crucial to ensure your pet's well-being. Here's a detailed guide on aftercare and monitoring for tick-related illnesses:
Aftercare Steps:
-
Wound Care: Keep a close eye on the bite site where the tick was removed. Clean the area with mild soap and water, and monitor for any signs of redness, swelling, or discharge. If you notice any concerning changes, consult your veterinarian promptly.
-
Prevent Licking or Scratching: Prevent your dog from licking or scratching the bite site excessively. If necessary, consider using an Elizabethan collar to discourage your pet from aggravating the area.
-
Watch for Allergic Reactions: Some dogs may exhibit allergic reactions to tick bites, leading to localized dermatitis and itching. Monitor for any signs of excessive itching, skin irritation, or hives, and seek veterinary advice if such symptoms arise.
-
Tick-Borne Disease Symptoms: Be vigilant for symptoms of tick-borne illnesses in your dog, such as fever, lethargy, lameness, and loss of appetite. Additionally, observe for any unusual behaviors or signs of discomfort that may indicate a potential health issue.
Monitoring Guidelines:
-
Daily Observation: In the days following tick removal, observe your dog daily for any changes in behavior, appetite, or physical condition. This regular monitoring allows for early detection of any abnormal symptoms.
-
Temperature Checks: Consider monitoring your dog's temperature using a rectal thermometer. A normal canine temperature ranges from 100.5°F to 102.5°F. Any significant deviation from this range warrants veterinary attention.
-
Consulting a Veterinarian: If you notice any concerning symptoms or changes in your dog's health post-tick removal, promptly seek professional veterinary guidance. Your veterinarian can conduct thorough assessments and diagnostic tests to rule out any potential tick-borne illnesses.
-
Tick-Borne Disease Testing: In some cases, your veterinarian may recommend specific blood tests to screen for tick-borne diseases, especially if your dog exhibits symptoms of illness. These tests can aid in early detection and appropriate management of any potential infections.
By diligently providing aftercare and closely monitoring your dog for tick-related illnesses, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your pet's health. Remember, early intervention and attentive care play a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with tick-borne diseases and ensuring your dog's continued well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of embedded ticks on dogs poses significant health risks, ranging from localized irritation to the potential transmission of serious tick-borne illnesses. As responsible pet owners, it is imperative to equip ourselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to safely remove ticks from our furry companions. By understanding the risks associated with embedded ticks and being prepared to address this issue effectively, we can prioritize our dogs' well-being and minimize the likelihood of tick-borne disease transmission.
The step-by-step guide provided in this article offers a comprehensive approach to safely removing embedded ticks from dogs. From preparing the area and using the right tools to aftercare and monitoring for tick-related illnesses, each step is designed to empower pet owners with the necessary skills to handle tick removal with confidence and precision. By following these guidelines, pet owners can take proactive measures to protect their dogs from the potential dangers posed by ticks.
Furthermore, the emphasis on aftercare and vigilant monitoring underscores the importance of post-removal measures in ensuring the dog's continued health. By closely observing the bite site, watching for allergic reactions, and monitoring for symptoms of tick-borne illnesses, pet owners can detect and address any potential health concerns promptly. This proactive approach is instrumental in mitigating the risks associated with tick-borne diseases and promoting the well-being of our canine companions.
Ultimately, the key takeaway from this guide is the significance of proactive and informed care when it comes to addressing embedded ticks on dogs. By arming ourselves with the knowledge and resources needed for safe tick removal and diligent aftercare, we can effectively safeguard our dogs from the potential health risks associated with tick infestations. Through attentiveness, preparedness, and a commitment to our pets' health, we can create a safe and nurturing environment for our beloved canine companions.
In essence, by prioritizing tick awareness and implementing the recommended guidelines, pet owners can play a pivotal role in protecting their dogs from the perils of tick-borne diseases. With the right knowledge and proactive measures in place, we can ensure that our dogs continue to thrive in a safe and healthy environment, free from the risks posed by embedded ticks.
