Home>Health & Wellness>Nutrition & Diet>What Type Of Diet Prevents Stones In Dogs’ Urine


Nutrition & Diet
What Type Of Diet Prevents Stones In Dogs’ Urine
Published: January 28, 2024
Learn how proper nutrition and diet can prevent stones in dogs' urine. Discover the best diet to keep your furry friend healthy and happy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Urinary stones in dogs can cause discomfort and distress, impacting their overall well-being. As a responsible pet owner, understanding the significance of diet in preventing urinary stones is crucial for maintaining your furry friend's health. By implementing dietary strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of urinary stones and ensure your dog's urinary system functions optimally.
Understanding the factors contributing to urinary stones and the role of diet in preventing their formation is essential for promoting your dog's urinary health. This article delves into the various types of urinary stones, the pivotal role of diet in mitigating their development, and the recommended dietary measures to safeguard your dog from this common ailment. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the intricate relationship between diet and urinary stone prevention, empowering you to make informed decisions for your beloved canine companion.
Understanding Urinary Stones in Dogs
Urinary stones, also known as uroliths, are crystalline structures that can form in the urinary tract of dogs. These stones can vary in size and composition, and they have the potential to cause discomfort, pain, and urinary tract obstruction. Understanding the nature of urinary stones is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and ensuring the well-being of your canine companion.
The formation of urinary stones in dogs is often attributed to various factors, including diet, genetics, and underlying medical conditions. The composition of these stones can differ, with some being predominantly made of minerals such as struvite, calcium oxalate, urate, cystine, or a combination of these substances. Each type of stone has distinct characteristics and may require specific dietary interventions for prevention.
When urinary stones develop, they can lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, straining to urinate, blood in the urine, and discomfort during urination. In severe cases, urinary stones may cause urinary blockages, which can be life-threatening if not promptly addressed. Therefore, recognizing the signs of urinary stones and understanding their underlying causes are essential for proactive management and prevention.
Moreover, certain breeds are predisposed to developing specific types of urinary stones due to genetic factors. For instance, Dalmatians are prone to urate stones, while Miniature Schnauzers and Bichon Frises are more susceptible to developing calcium oxalate stones. By being aware of breed-specific tendencies, pet owners can take proactive measures to mitigate the risk of urinary stone formation through tailored dietary approaches and regular veterinary monitoring.
In summary, comprehending the nature of urinary stones in dogs is pivotal for identifying potential risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and implementing preventive measures. By gaining insights into the underlying causes and characteristics of urinary stones, pet owners can take proactive steps to safeguard their furry companions from this common urinary ailment.
Common Types of Urinary Stones
Urinary stones in dogs can manifest in various compositions, each with distinct characteristics and dietary considerations. Understanding the common types of urinary stones is essential for tailoring preventive dietary measures to mitigate the risk of stone formation in your canine companion.
-
Struvite Stones: These stones, also known as magnesium ammonium phosphate stones, are one of the most prevalent types found in dogs. Struvite stones often develop in alkaline urine and are commonly associated with urinary tract infections. Their formation is influenced by the presence of certain bacteria that can elevate urine pH, leading to the precipitation of struvite crystals. Dietary management plays a crucial role in preventing the recurrence of struvite stones, typically involving the implementation of specific feeding regimens and the use of prescription diets formulated to dissolve and prevent their formation.
-
Calcium Oxalate Stones: Calcium oxalate stones are another common type found in dogs' urinary tracts. These stones are characterized by their hard, crystalline structure and are more likely to form in acidic urine. Certain breeds, such as Miniature Schnauzers and Lhasa Apsos, are predisposed to developing calcium oxalate stones. Dietary strategies for preventing calcium oxalate stones often focus on reducing the dietary intake of oxalate-rich foods and maintaining appropriate hydration levels to dilute urine and minimize the risk of stone formation.
-
Urate Stones: Urate stones, composed of uric acid crystals, can occur in dogs with specific genetic predispositions, such as Dalmatians and English Bulldogs. These breeds have a reduced ability to metabolize uric acid, leading to its accumulation in the urine and subsequent formation of urate stones. Dietary management for preventing urate stones typically involves minimizing purine-rich foods, as purines are metabolized into uric acid. Additionally, promoting urine alkalization through diet can help prevent the formation of urate stones.
-
Cystine Stones: Cystine stones are relatively rare but can occur in certain dog breeds with an inherited metabolic disorder known as cystinuria. This condition impairs the reabsorption of cystine in the kidneys, leading to its excessive excretion in the urine and subsequent formation of cystine stones. Dietary interventions for preventing cystine stones often focus on reducing the dietary intake of cystine and promoting urine dilution through increased water consumption.
Understanding the distinct characteristics and dietary considerations associated with each type of urinary stone is pivotal for implementing targeted preventive measures. By tailoring the diet to mitigate the specific risk factors associated with the formation of different types of urinary stones, pet owners can effectively safeguard their dogs from this common urinary ailment.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Urinary Stones
Diet plays a pivotal role in preventing the formation of urinary stones in dogs, serving as a fundamental component of proactive management and long-term urinary health. By understanding the intricate relationship between dietary factors and urinary stone formation, pet owners can implement targeted feeding regimens to mitigate the risk of stone development and recurrence.
The composition of a dog's diet significantly influences the pH and mineral content of their urine, directly impacting the formation of urinary stones. For instance, the pH level of urine plays a crucial role in determining the propensity for certain types of stones to form. By selecting appropriate dietary components, pet owners can effectively modulate urine pH to create an environment that discourages the crystallization of stone-forming minerals.
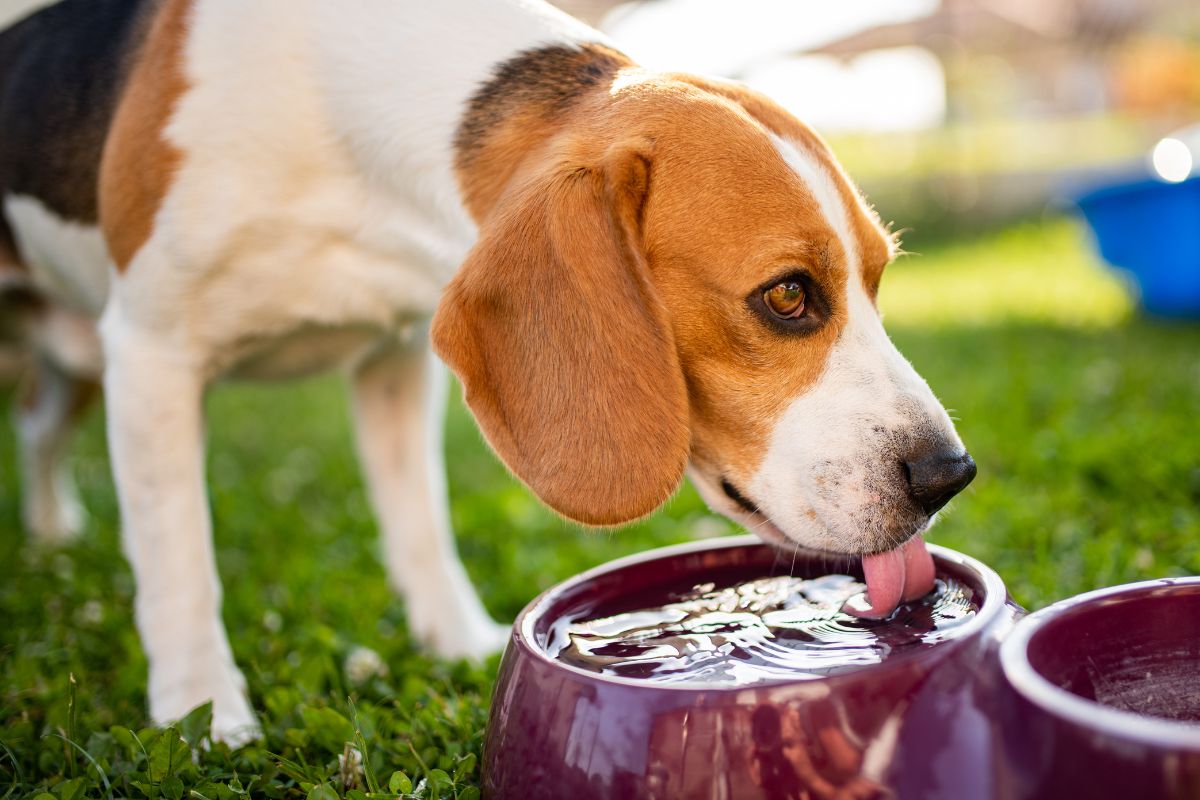
In addition to urine pH, the mineral content of the diet, particularly the levels of magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus, can profoundly influence the formation of urinary stones. Specific dietary formulations are designed to restrict the concentration of these minerals, thereby reducing the likelihood of stone precipitation in the urinary tract. Furthermore, adequate hydration through moisture-rich diets or access to fresh water is essential for promoting urine dilution, which can help prevent the crystallization of minerals and the subsequent formation of stones.
Moreover, the role of dietary protein and its impact on urinary stone formation should not be overlooked. Certain types of dietary proteins contain purines, which can be metabolized into uric acid, a precursor to urate stones. By carefully selecting protein sources and moderating their purine content, pet owners can effectively manage the risk of urate stone formation in breeds predisposed to this type of urinary stone.
Furthermore, the implementation of prescription diets formulated to dissolve existing stones or prevent their recurrence is a valuable strategy in urinary stone management. These specialized diets are tailored to address specific urinary stone compositions and risk factors, providing a comprehensive approach to dietary intervention for urinary stone prevention.
In essence, the role of diet in preventing urinary stones is multifaceted, encompassing the modulation of urine pH, restriction of stone-forming minerals, promotion of urine dilution, and strategic management of dietary protein. By leveraging the power of tailored nutrition, pet owners can proactively safeguard their dogs from the discomfort and health implications associated with urinary stone formation.
Recommended Diet for Preventing Urinary Stones
When it comes to preventing urinary stones in dogs, implementing a carefully curated diet is paramount. The following dietary recommendations are tailored to address the specific needs of dogs at risk of urinary stone formation, encompassing various aspects of nutrition to promote urinary health and minimize the likelihood of stone development.
Read more: What Type Of Chews Are Best For A Senior Dog
1. Moisture-Rich Foods:
Incorporating moisture-rich foods into your dog's diet is essential for promoting adequate hydration, which plays a pivotal role in preventing urinary stone formation. Wet or canned dog food, supplemented with fresh vegetables and fruits, can contribute to increased water intake and urine dilution, thereby reducing the concentration of stone-forming minerals in the urinary tract.
2. Controlled Mineral Levels:
Selecting dog foods with controlled levels of minerals, including magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus, is crucial for mitigating the risk of urinary stone formation. These specialized diets are formulated to restrict the concentration of minerals known to contribute to stone precipitation, creating an environment less conducive to the development of urinary stones.
3. pH-Modifying Ingredients:
Incorporating pH-modifying ingredients into your dog's diet can help create an environment in the urinary tract that discourages the formation of specific types of urinary stones. For instance, diets formulated to prevent struvite stone formation often contain ingredients that promote urine acidification, while those aimed at preventing calcium oxalate stones may focus on maintaining a slightly alkaline urine pH.
4. Prescription Diets:
Consulting with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable prescription diet for your dog's specific urinary health needs is highly recommended. Prescription diets are tailored to address the underlying factors contributing to urinary stone formation, such as the presence of certain minerals or the pH of the urine. These specialized diets are designed to dissolve existing stones or prevent their recurrence, providing comprehensive dietary intervention for urinary stone prevention.
5. Protein Management:
Carefully managing the protein content of your dog's diet is essential, especially for breeds predisposed to urate stone formation. Selecting protein sources with lower purine content can help mitigate the risk of uric acid crystal formation, contributing to the prevention of urate stones.
By incorporating these dietary recommendations into your dog's feeding regimen, you can proactively promote urinary health and reduce the likelihood of urinary stone formation. However, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate dietary approach based on your dog's specific health status, breed predispositions, and urinary stone risk factors. With a tailored and proactive approach to nutrition, you can effectively safeguard your canine companion from the discomfort and health implications associated with urinary stones.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the prevention of urinary stones in dogs is intricately linked to dietary management, emphasizing the pivotal role of nutrition in promoting urinary health and mitigating the risk of stone formation. By understanding the diverse types of urinary stones and their associated dietary considerations, pet owners can proactively implement targeted feeding regimens to safeguard their canine companions from this common urinary ailment.
The multifaceted nature of dietary interventions for urinary stone prevention encompasses various aspects, including urine pH modulation, controlled mineral levels, hydration promotion, and strategic protein management. By incorporating moisture-rich foods, controlled mineral levels, pH-modifying ingredients, and prescription diets into their dog's feeding regimen, pet owners can create an environment in the urinary tract that discourages the formation of specific types of urinary stones.
Furthermore, the tailored approach to nutrition extends to breed-specific considerations, acknowledging the genetic predispositions of certain breeds to develop distinct types of urinary stones. By recognizing these breed-specific tendencies and implementing targeted dietary measures, pet owners can effectively mitigate the risk of stone formation and promote the overall urinary health of their beloved canine companions.
Consulting with a veterinarian is paramount in devising a comprehensive dietary strategy for urinary stone prevention, as it allows for personalized recommendations based on the dog's specific health status, breed predispositions, and urinary stone risk factors. The expertise of a veterinarian enables pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog's nutrition, ensuring that the dietary approach aligns with the unique needs and health considerations of their furry companions.
In essence, the proactive management of urinary stone formation through dietary interventions empowers pet owners to take an active role in promoting their dog's urinary health and well-being. By leveraging the power of tailored nutrition and seeking professional guidance, pet owners can navigate the complexities of urinary stone prevention with confidence, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for their canine companions.