Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Muscular and Joint Health>How Do Dogs Get Septic Arthritis


Muscular and Joint Health
How Do Dogs Get Septic Arthritis
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how dogs develop septic arthritis and how to support their muscular and joint health. Discover effective strategies for preventing and managing this condition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Septic arthritis, also known as infectious or bacterial arthritis, is a serious and painful condition that can affect dogs of all ages and breeds. This inflammatory joint disease occurs when harmful bacteria, such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, invade a dog's joint, leading to infection and subsequent inflammation. The resulting discomfort and restricted mobility can significantly impact a dog's quality of life, making it crucial for pet owners to recognize the signs and seek prompt veterinary care.
Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for septic arthritis in dogs is essential for ensuring the well-being of our beloved canine companions. By delving into these aspects, we can gain valuable insights into this condition and learn how to effectively prevent and manage it. Let's explore the intricacies of septic arthritis in dogs, shedding light on the various facets of this debilitating ailment and empowering pet owners with the knowledge needed to safeguard their furry friends' joint health.
Read more: What Age Do Dogs Get Arthritis
Understanding Septic Arthritis in Dogs
Septic arthritis in dogs is a severe and debilitating condition characterized by the invasion of harmful bacteria into a dog's joint, leading to infection and inflammation. This bacterial invasion can occur through various means, such as penetrating wounds, surgical procedures, or the spread of bacteria from other parts of the body. Once inside the joint, the bacteria trigger an immune response, causing the release of inflammatory substances that lead to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
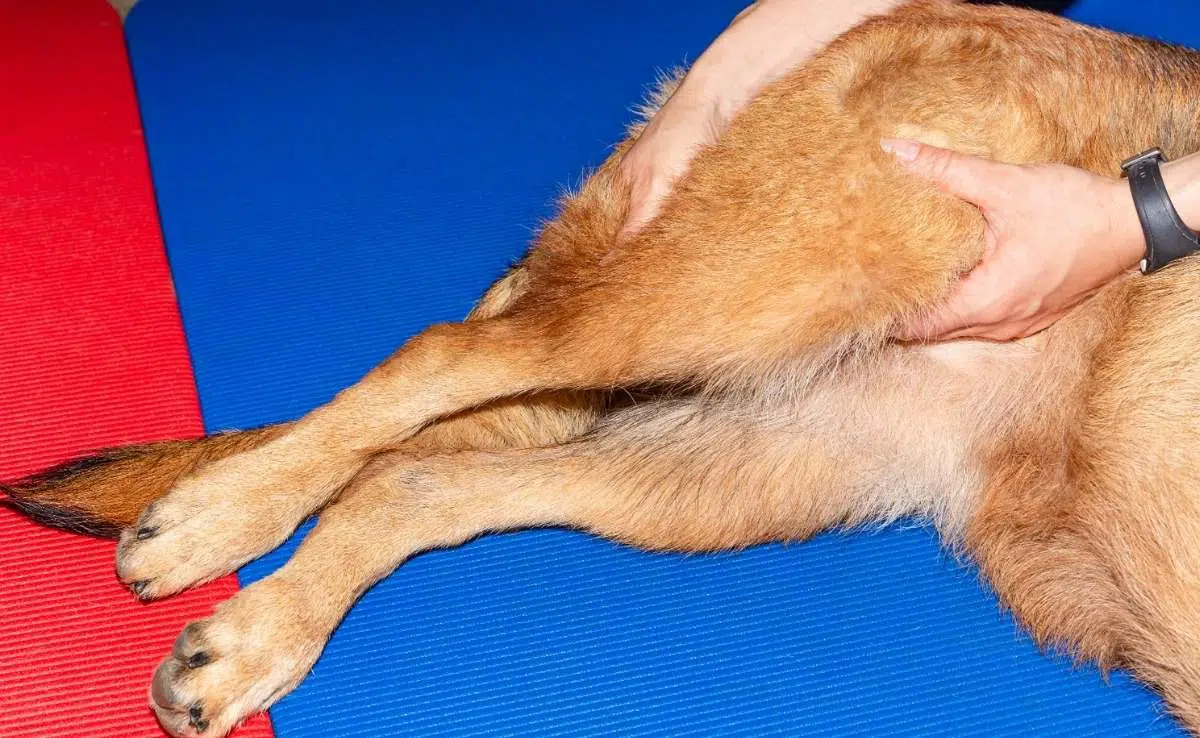
The joints most commonly affected by septic arthritis in dogs are the hips, knees, elbows, and shoulders. These are weight-bearing joints that are crucial for a dog's mobility and overall well-being. When infected, these joints become inflamed, causing intense discomfort and hindering the dog's ability to move freely. As a result, affected dogs may exhibit signs of lameness, reluctance to bear weight on the affected limb, and visible joint swelling.
It's important to note that septic arthritis differs from other forms of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or immune-mediated arthritis, as it is primarily caused by a bacterial infection. This key distinction underscores the urgent need for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment to address the underlying infection and alleviate the associated inflammation.
Furthermore, septic arthritis can have systemic effects on a dog's health, potentially leading to fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite. These systemic symptoms often accompany the localized joint manifestations, signaling the body's broader response to the bacterial invasion.
Understanding the intricacies of septic arthritis in dogs is crucial for pet owners and veterinarians alike. By recognizing the distinct nature of this condition and its impact on a dog's joint health and overall well-being, proactive measures can be taken to mitigate the risk of infection and promptly address any suspected cases. Through heightened awareness and a deeper understanding of septic arthritis, we can work towards safeguarding our canine companions from this debilitating ailment.
Causes of Septic Arthritis in Dogs
Septic arthritis in dogs can arise from various sources, with bacterial infections being the primary instigators of this debilitating condition. Understanding the specific causes and risk factors associated with septic arthritis is pivotal in implementing preventive measures and promoting proactive joint health in dogs.
-
Bacterial Invasion: The most common cause of septic arthritis in dogs is the infiltration of bacteria into the joint space. This can occur through penetrating wounds, traumatic injuries, or post-surgical complications. Bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are frequent culprits, gaining access to the joint and inciting an inflammatory response.
-
Hematogenous Spread: In some cases, bacteria may enter a dog's joint via the bloodstream, a process known as hematogenous spread. This can happen when a dog has an existing bacterial infection elsewhere in the body, and the pathogens travel through the bloodstream to settle in the joint, triggering an infectious process.
-
Joint Surgery or Injections: Dogs that undergo joint surgeries or receive intra-articular injections are at an increased risk of developing septic arthritis. While these procedures are often performed to address existing joint issues, they can inadvertently introduce bacteria into the joint space, leading to infection and subsequent inflammation.
-
Immune System Compromise: Dogs with weakened immune systems, whether due to underlying medical conditions or immunosuppressive medications, are more susceptible to bacterial infections, including those that can cause septic arthritis. A compromised immune response may struggle to combat invading pathogens effectively, allowing them to proliferate and incite joint infection.
-
Pre-existing Joint Conditions: Dogs with pre-existing joint ailments, such as osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, may be at a higher risk of developing septic arthritis. The compromised integrity of the joint structures in these conditions can create an environment conducive to bacterial colonization and infection.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental elements, such as unhygienic living conditions, exposure to contaminated water sources, or contact with infected animals, can contribute to the development of septic arthritis in dogs. These external factors can introduce pathogenic bacteria into a dog's environment, increasing the likelihood of joint infection.
By recognizing these diverse causes and risk factors, pet owners and veterinarians can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of septic arthritis in dogs. Implementing stringent hygiene practices, promptly addressing traumatic injuries, and closely monitoring dogs with pre-existing joint conditions are essential measures in safeguarding canine joint health and mitigating the potential impact of septic arthritis.
Symptoms of Septic Arthritis in Dogs
Recognizing the symptoms of septic arthritis in dogs is crucial for early detection and intervention. This debilitating condition manifests through a range of clinical signs, signaling the presence of joint infection and inflammation. By understanding these symptoms, pet owners and veterinarians can promptly address suspected cases of septic arthritis, alleviating the dog's discomfort and preventing potential complications.
-
Lameness and Reluctance to Bear Weight: Dogs affected by septic arthritis often exhibit lameness, favoring the unaffected limbs and displaying reluctance to bear weight on the affected limb. This reluctance may be particularly noticeable during physical activity or when rising from a resting position.
-
Joint Swelling and Pain: Swelling and pain in the affected joint are hallmark symptoms of septic arthritis. The joint may appear visibly swollen, accompanied by tenderness and discomfort when touched. Dogs may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as vocalization or withdrawal, when the affected joint is manipulated or palpated.
-
Limited Range of Motion: Infected joints can restrict a dog's range of motion, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility. Dogs may struggle to move the affected limb freely, displaying hesitancy or difficulty when attempting to perform regular activities such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
-
Systemic Signs of Infection: In addition to localized joint symptoms, dogs with septic arthritis may display systemic signs of infection, including fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite. These systemic manifestations reflect the body's response to the bacterial invasion and underscore the severity of the condition.
-
Heat and Redness: The affected joint may exhibit warmth and redness, indicative of the inflammatory response triggered by the bacterial infection. These visible signs of inflammation can be observed during physical examination, aiding in the identification of septic arthritis in dogs.
-
Behavioral Changes: Dogs suffering from septic arthritis may demonstrate changes in behavior, such as increased restlessness, irritability, or a reluctance to engage in activities they previously enjoyed. These behavioral alterations can stem from the discomfort and physical limitations imposed by the joint infection.
-
Joint Effusion: Effusion, or the accumulation of fluid within the joint space, is a common feature of septic arthritis. This fluid buildup contributes to joint swelling and may be palpable during veterinary examination, providing valuable diagnostic clues.
By remaining vigilant for these symptoms, pet owners can promptly seek veterinary evaluation if they suspect their dog may be suffering from septic arthritis. Early recognition and intervention are pivotal in managing this condition effectively, minimizing the impact on the dog's joint health and overall well-being. Through heightened awareness and proactive monitoring, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions from the debilitating effects of septic arthritis.
Diagnosing Septic Arthritis in Dogs
Accurate and timely diagnosis of septic arthritis in dogs is essential for implementing targeted treatment and mitigating the potential impact of this debilitating condition on a dog's joint health. Veterinary professionals employ a multifaceted approach to diagnose septic arthritis, encompassing clinical evaluation, diagnostic imaging, joint fluid analysis, and microbial testing. By integrating these diagnostic modalities, veterinarians can effectively identify septic arthritis and differentiate it from other joint disorders, enabling tailored therapeutic interventions.
Read more: How Dogs Get Arthritis
Clinical Evaluation
The diagnostic process often commences with a comprehensive clinical assessment of the affected dog. Veterinarians meticulously evaluate the dog's gait, joint mobility, and overall demeanor, paying close attention to signs of lameness, joint swelling, and discomfort. Additionally, the dog's medical history, including any recent injuries, surgeries, or existing joint conditions, is thoroughly reviewed to glean valuable insights into potential predisposing factors for septic arthritis.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as radiography (X-rays) and advanced imaging modalities like ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a pivotal role in the diagnostic workup for septic arthritis. These imaging studies provide detailed visualization of the affected joint, facilitating the identification of characteristic changes associated with joint infection, such as soft tissue swelling, joint effusion, and bony abnormalities. Moreover, imaging aids in ruling out alternative causes of joint pathology, contributing to a more precise diagnosis.
Joint Fluid Analysis
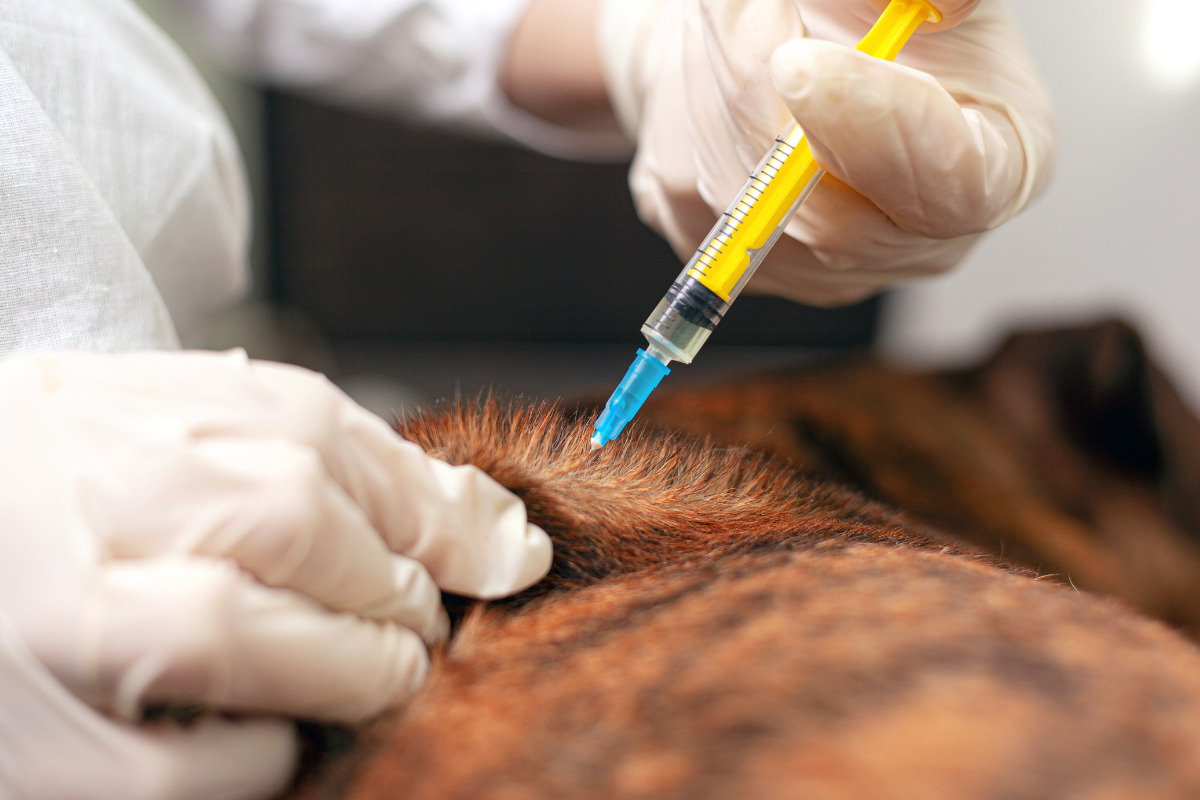
Aspiration and analysis of joint fluid, known as arthrocentesis, represent a fundamental component of diagnosing septic arthritis in dogs. During arthrocentesis, a small sample of synovial fluid is extracted from the affected joint and subjected to thorough analysis. The fluid is evaluated for its appearance, viscosity, cell count, protein content, and the presence of inflammatory markers. In cases of septic arthritis, the joint fluid may exhibit purulent (pus-filled) characteristics, elevated white blood cell count, and bacterial presence, indicative of an infectious process within the joint.
Microbial Testing
Microbial testing, including bacterial culture and sensitivity analysis, is instrumental in confirming the presence of pathogenic bacteria within the affected joint. The isolated bacteria are cultured in a laboratory setting to identify the specific infectious agents and determine their susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. This information is invaluable for guiding targeted antibiotic therapy, ensuring effective eradication of the causative bacteria and resolution of the joint infection.
By integrating these diagnostic approaches, veterinarians can establish a definitive diagnosis of septic arthritis in dogs, enabling the formulation of a tailored treatment plan to address the underlying infection and alleviate the associated joint inflammation. The comprehensive nature of the diagnostic process underscores the importance of veterinary expertise in identifying and managing septic arthritis, ultimately promoting optimal joint health and well-being in affected dogs.
Treatment for Septic Arthritis in Dogs
The treatment of septic arthritis in dogs necessitates a comprehensive and multifaceted approach aimed at eradicating the underlying infection, alleviating joint inflammation, and restoring optimal joint function. Veterinary intervention is pivotal in guiding the therapeutic process, encompassing targeted antimicrobial therapy, joint lavage, supportive care, and rehabilitative measures to facilitate the dog's recovery.
Antimicrobial Therapy
Prompt initiation of antimicrobial therapy is imperative in combating the infectious agents responsible for septic arthritis. Veterinarians prescribe broad-spectrum or culture-specific antibiotics based on the results of microbial testing, tailoring the treatment to effectively target the identified bacteria. The selected antibiotics are administered at appropriate dosages and durations to ensure optimal efficacy and resolution of the joint infection. Close monitoring of the dog's response to antimicrobial therapy is essential, with periodic re-evaluation to assess treatment progress and adjust the regimen as needed.
Joint Lavage
Joint lavage, also known as arthroscopic lavage or irrigation, involves the thorough cleansing of the infected joint to remove purulent material, inflammatory debris, and infectious agents. This procedure is performed under anesthesia, allowing veterinarians to access the affected joint and irrigate it with sterile fluid to eliminate the infectious burden. Joint lavage serves to mitigate the inflammatory response, alleviate joint pain, and facilitate the penetration of antimicrobial agents into the joint space, promoting effective bacterial eradication.
Supportive Care
Dogs afflicted with septic arthritis require attentive supportive care to address their pain, discomfort, and systemic manifestations of infection. Veterinarians may prescribe analgesic medications to alleviate joint pain and inflammation, enhancing the dog's comfort and mobility. Additionally, supportive measures such as rest, joint immobilization, and dietary support are implemented to promote the dog's overall well-being and aid in the resolution of the joint infection.
Read more: How Do Indoor Dogs Get Fleas
Rehabilitation and Monitoring
Following the acute phase of treatment, rehabilitative measures play a crucial role in restoring the affected joint's function and promoting the dog's physical recovery. Physical therapy, controlled exercise regimens, and joint mobilization techniques are employed to prevent joint stiffness, muscle atrophy, and promote optimal healing. Regular veterinary monitoring is essential to assess the dog's response to treatment, monitor joint health, and ensure the successful resolution of septic arthritis.
By integrating these therapeutic modalities, veterinarians strive to address the multifaceted aspects of septic arthritis in dogs, working towards the eradication of infection, alleviation of joint inflammation, and restoration of optimal joint function. The collaborative efforts of pet owners and veterinary professionals are instrumental in facilitating the dog's recovery and promoting long-term joint health, underscoring the significance of proactive management and comprehensive care in mitigating the impact of septic arthritis.
Preventing Septic Arthritis in Dogs
Preventing septic arthritis in dogs encompasses a proactive and multifaceted approach aimed at minimizing the risk of joint infections and promoting optimal joint health. By implementing stringent hygiene practices, addressing predisposing factors, and prioritizing preventive veterinary care, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions from this debilitating condition.
Hygiene and Wound Care
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment for dogs is fundamental in preventing septic arthritis. Regularly cleaning and disinfecting living spaces, bedding, and grooming equipment helps mitigate the risk of bacterial contamination. Additionally, prompt and thorough wound care is essential for preventing the entry of pathogens into the body, reducing the likelihood of joint infections stemming from traumatic injuries or surgical incisions.
Joint Health Management
Proactively managing a dog's joint health is crucial in minimizing the risk of septic arthritis. This includes maintaining a healthy weight to alleviate undue stress on the joints, providing balanced nutrition to support joint integrity, and incorporating regular exercise to promote joint mobility and muscle strength. Furthermore, addressing pre-existing joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis, through veterinary guidance and appropriate management strategies can help mitigate the predisposition to joint infections.
Read more: How Do Dogs Get Urinary Crystals?
Injury Prevention and Monitoring
Preventing traumatic injuries and minimizing exposure to potential sources of infection are integral components of septic arthritis prevention. Pet owners should take proactive measures to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries, such as providing a safe and secure environment, using appropriate restraints during travel, and supervising dogs during outdoor activities. Additionally, vigilant monitoring for signs of injury or joint discomfort enables early intervention, reducing the likelihood of subsequent joint infections.
Veterinary Care and Vaccination
Regular veterinary check-ups and preventive care are essential for promoting overall canine health and mitigating the risk of infectious diseases. Maintaining up-to-date vaccinations, including those targeting bacterial pathogens, can bolster a dog's immune defenses against potential joint-infecting agents. Furthermore, seeking prompt veterinary attention for any signs of joint abnormalities, lameness, or systemic illness enables early detection and intervention, preventing the progression of joint infections.
Surgical and Procedural Considerations
For dogs undergoing joint surgeries or receiving intra-articular injections, adherence to stringent aseptic techniques and post-operative care protocols is paramount in preventing iatrogenic joint infections. Pet owners should seek reputable veterinary professionals and facilities with robust infection control measures to minimize the risk of post-procedural complications, including septic arthritis.
By integrating these preventive measures into their canine care routines, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of septic arthritis in dogs, fostering optimal joint health and overall well-being. The proactive management of hygiene, joint health, injury prevention, and veterinary oversight collectively contributes to a comprehensive approach to septic arthritis prevention, underscoring the importance of proactive and attentive care in safeguarding canine joint health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, septic arthritis poses a significant threat to the joint health and overall well-being of dogs, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and preventive strategies. This debilitating condition, characterized by bacterial invasion and joint infection, can profoundly impact a dog's mobility, comfort, and quality of life. By delving into the intricacies of septic arthritis, pet owners and veterinary professionals can equip themselves with the knowledge and proactive measures needed to safeguard canine companions from this formidable ailment.
Recognizing the diverse causes of septic arthritis, ranging from bacterial infiltration to immune system compromise, underscores the multifaceted nature of this condition. Environmental factors, pre-existing joint conditions, and surgical interventions all contribute to the risk of joint infection, emphasizing the importance of proactive hygiene, injury prevention, and vigilant veterinary oversight. By addressing these predisposing factors and prioritizing joint health management, pet owners can play a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of septic arthritis in their dogs.
The identification of septic arthritis hinges on the recognition of its hallmark symptoms, including lameness, joint swelling, limited mobility, and systemic signs of infection. Early detection and prompt veterinary evaluation are paramount in initiating targeted diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, enabling the effective management of septic arthritis and the restoration of joint health in affected dogs.
The diagnostic process, encompassing clinical evaluation, diagnostic imaging, joint fluid analysis, and microbial testing, serves as a cornerstone in confirming septic arthritis and guiding tailored treatment strategies. Through the integration of these diagnostic modalities, veterinarians can accurately identify joint infections, differentiate them from other joint disorders, and implement targeted therapeutic interventions to address the underlying infection and alleviate joint inflammation.
The treatment of septic arthritis necessitates a multifaceted approach, encompassing antimicrobial therapy, joint lavage, supportive care, and rehabilitative measures to facilitate the dog's recovery and restore optimal joint function. By collaborating with veterinary professionals and adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, pet owners can actively contribute to their dog's healing process and long-term joint health.
Preventive measures, including stringent hygiene practices, injury prevention, joint health management, and proactive veterinary care, form the cornerstone of septic arthritis prevention in dogs. By integrating these proactive measures into their canine care routines, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of septic arthritis, fostering optimal joint health and overall well-being in their beloved companions.
In essence, a comprehensive understanding of septic arthritis, coupled with proactive management and attentive care, empowers pet owners to safeguard their dogs from the debilitating effects of joint infection. By prioritizing joint health, implementing preventive strategies, and seeking prompt veterinary attention when needed, pet owners can play a pivotal role in promoting optimal joint health and well-being in their canine companions, ensuring a fulfilling and active lifestyle for their beloved pets.