Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How To Test Your Dog For Food Allergies


Common Health Issues
How To Test Your Dog For Food Allergies
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how to test your dog for food allergies and address common health issues. Keep your furry friend happy and healthy with these tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Food allergies are not limited to humans; our canine companions can also suffer from this condition. Just like people, dogs can develop adverse reactions to certain foods, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. As a responsible pet owner, it's essential to be aware of the signs of food allergies in dogs and understand the testing methods available to diagnose these allergies accurately.
Identifying and addressing food allergies in dogs is crucial for their overall well-being. By gaining insights into the common allergens and testing procedures, you can take proactive steps to ensure your furry friend's health and happiness.
Understanding the nuances of food allergies in dogs and the available testing methods can empower you to make informed decisions about your pet's diet and healthcare. This article will delve into the signs and symptoms of food allergies in dogs, explore the common allergens that affect them, and discuss the various testing methods available to diagnose food allergies in dogs accurately. Let's embark on this journey to equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to support our canine companions in leading healthy and allergy-free lives.
Read more: How Can I Test For Dog Allergies
Understanding Food Allergies in Dogs
Food allergies in dogs occur when their immune systems react abnormally to specific ingredients in their diet. Unlike food intolerances, which typically result in digestive issues, food allergies prompt an immune system response, leading to a range of symptoms. These allergies can develop over time, even if a dog has been consuming the same food for years without any adverse effects.
The proteins in certain foods are often the primary culprits behind food allergies in dogs. When a dog's immune system identifies these proteins as harmful, it triggers an allergic reaction. Common food allergens for dogs include beef, dairy, wheat, egg, chicken, lamb, soy, pork, rabbit, and fish. Additionally, dogs can develop allergies to certain grains, such as corn, soy, and wheat, as well as artificial additives and preservatives found in commercial pet foods.
It's important to note that food allergies differ from environmental allergies, which are typically triggered by pollen, dust mites, or mold. While environmental allergies often manifest as skin irritations and respiratory issues, food allergies can lead to a broader spectrum of symptoms, affecting the skin, digestive system, and overall well-being of the dog.
When a dog ingests a food allergen, the immune system releases histamines and other chemicals, leading to various allergic reactions. These reactions can manifest as itching, skin rashes, hives, ear infections, gastrointestinal problems, chronic diarrhea, vomiting, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
Understanding the intricacies of food allergies in dogs is crucial for pet owners. By recognizing the potential triggers and symptoms of food allergies, you can take proactive measures to address and manage these conditions effectively. Additionally, being aware of the common food allergens for dogs and the impact of these allergies on their health empowers pet owners to make informed decisions about their furry companions' diet and overall well-being.
Signs and Symptoms of Food Allergies in Dogs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of food allergies in dogs is crucial for pet owners to provide timely intervention and relief for their furry companions. While the manifestations of food allergies can vary among individual dogs, several common symptoms indicate a potential allergic reaction to certain foods.
-
Skin Irritations: One of the most prevalent indicators of food allergies in dogs is skin-related issues. These may include persistent itching, redness, and inflammation, often leading to frequent scratching, licking, or chewing of the affected areas. Skin rashes, hives, and hot spots can also develop, causing discomfort and distress for the dog.
-
Gastrointestinal Distress: Dogs with food allergies may experience digestive problems, such as chronic diarrhea, vomiting, and excessive gas. These symptoms can significantly impact the dog's overall well-being and may lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies if left unaddressed.
-
Ear Infections: Food allergies can contribute to the development of ear infections in dogs. Persistent scratching of the ears, foul odor, redness, and discharge may indicate an allergic reaction to certain food ingredients.
-
Chronic Itching and Hair Loss: Dogs suffering from food allergies often exhibit chronic itching, particularly around the face, paws, ears, and abdomen. This incessant scratching can lead to hair loss and the formation of irritated, inflamed patches on the skin.
-
Respiratory Issues: In some cases, food allergies can manifest as respiratory problems in dogs, including sneezing, coughing, and wheezing. While less common than skin and gastrointestinal symptoms, respiratory issues should not be overlooked as potential signs of food allergies.
It's important to note that the onset of these symptoms may not be immediate after consuming the allergenic food. In some cases, the allergic reactions may take hours or even days to become apparent, making it challenging for pet owners to pinpoint the specific trigger without proper testing.
By being attentive to these signs and symptoms, pet owners can collaborate with veterinarians to conduct comprehensive testing and identify the specific food allergens affecting their dogs. This proactive approach enables the implementation of tailored dietary plans and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate the discomfort caused by food allergies and enhance the overall well-being of canine companions.
Common Food Allergens for Dogs
Understanding the common food allergens for dogs is essential for pet owners to identify potential triggers and make informed decisions about their furry companions' diet. While dogs can develop allergies to various food ingredients, certain allergens are more prevalent in triggering adverse reactions. By familiarizing ourselves with these common food allergens, we can take proactive measures to minimize the risk of allergic reactions in our canine friends.
-
Beef: Beef is a common allergen for dogs, often leading to skin irritations, digestive issues, and respiratory problems. The proteins in beef can trigger an immune system response, prompting allergic reactions in susceptible dogs.
-
Dairy: Dairy products, including milk and cheese, can elicit allergic reactions in dogs. Lactose intolerance is also prevalent among canines, leading to digestive discomfort and gastrointestinal distress.
-
Wheat: Wheat and wheat-based products are known allergens for dogs, contributing to skin rashes, itching, and digestive disturbances. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, can be particularly problematic for dogs with sensitivities.
-
Egg: Eggs are a common source of protein in many dog foods, but they can also be a potential allergen. Allergic reactions to eggs can manifest as skin irritations, gastrointestinal issues, and respiratory symptoms in dogs.
-
Chicken: While chicken is a popular protein source in dog diets, some dogs may develop allergies to chicken proteins. Allergic reactions to chicken can result in skin rashes, itching, and digestive discomfort.
-
Lamb: Lamb is another protein source that can trigger allergic reactions in dogs. Dogs with sensitivities to lamb may experience skin irritations, gastrointestinal disturbances, and respiratory issues upon consumption.
-
Soy: Soy and soy-based products are known allergens for dogs, often leading to skin problems, digestive issues, and allergic reactions. Soy proteins can prompt immune system responses, causing discomfort for susceptible dogs.
-
Fish: While fish is a valuable source of omega-3 fatty acids for dogs, it can also be an allergen for some individuals. Allergic reactions to fish may manifest as skin irritations, itching, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
-
Corn: Corn and corn-derived ingredients are common allergens for dogs, contributing to skin rashes, itching, and digestive discomfort. Dogs with sensitivities to corn may exhibit allergic reactions upon consuming foods containing this ingredient.
-
Artificial Additives: Artificial additives and preservatives found in commercial pet foods can also trigger allergic reactions in dogs. These additives may include artificial colors, flavors, and chemical preservatives, leading to various allergic symptoms.
By being aware of these common food allergens for dogs, pet owners can make informed choices when selecting and managing their pets' diets. Additionally, understanding the potential triggers for food allergies empowers pet owners to collaborate with veterinarians to conduct comprehensive testing and implement tailored dietary plans to address and manage allergic reactions effectively.
Testing Methods for Food Allergies in Dogs
Accurately diagnosing food allergies in dogs is essential for implementing targeted dietary plans and alleviating the discomfort caused by allergic reactions. Several testing methods are available to identify specific food allergens affecting dogs, enabling pet owners and veterinarians to make informed decisions about their pets' health and well-being.
Elimination Diet
The elimination diet is a primary method for diagnosing food allergies in dogs. This approach involves removing all potential allergens from the dog's diet and replacing them with novel protein and carbohydrate sources that the dog has not been previously exposed to. Common novel protein sources include venison, duck, rabbit, and kangaroo, while alternative carbohydrate sources may include sweet potatoes, peas, and tapioca. By feeding the dog this limited ingredient diet for a specified period, typically 8 to 12 weeks, pet owners can observe any improvements in the dog's symptoms, indicating a potential food allergy. If the symptoms subside during the elimination diet phase and reappear upon reintroducing specific foods, it can help identify the allergenic ingredients triggering the dog's allergic reactions.
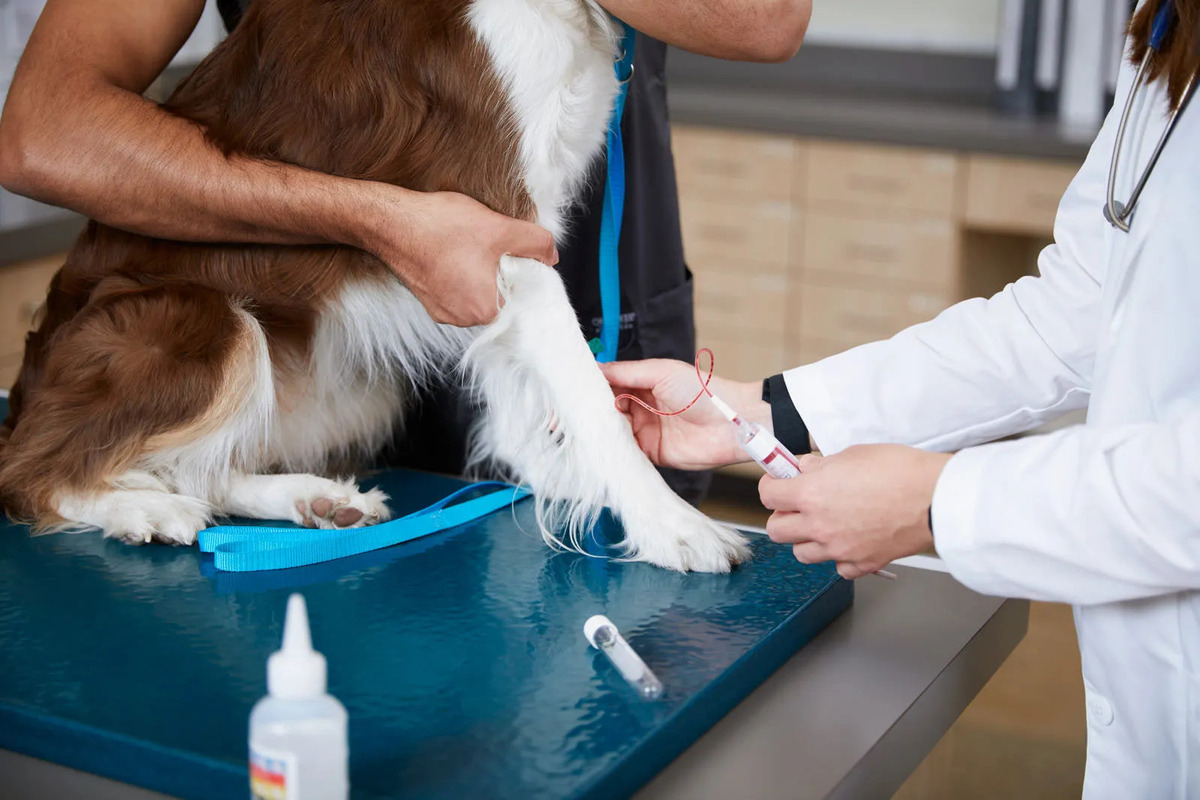
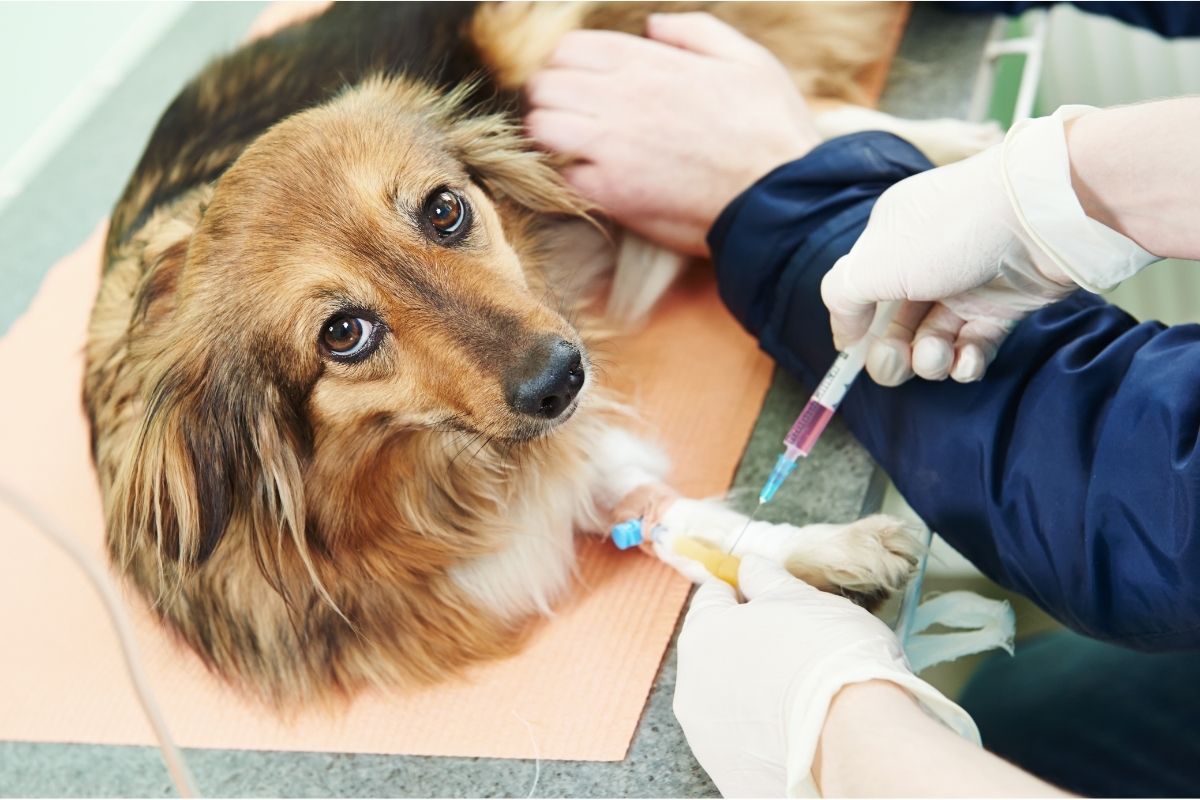
Blood Tests
Blood tests, such as serum allergy testing, can also aid in identifying food allergens affecting dogs. These tests measure the levels of specific antibodies, including immunoglobulin E (IgE), in the dog's blood in response to various food proteins. Elevated levels of specific antibodies can indicate the presence of food allergies, providing insights into the potential allergens affecting the dog. While blood tests can offer valuable information about the dog's immune response to certain foods, it's essential to interpret the results in conjunction with the dog's clinical symptoms and dietary history for accurate diagnosis.
Skin Tests
Intradermal skin testing, commonly used to diagnose environmental allergies in dogs, can also be employed to identify food allergens. During this procedure, small amounts of food allergens are injected into the dog's skin, and any resulting allergic reactions, such as redness or swelling, are observed. While skin tests can provide insights into potential food allergens, they may carry a risk of false-positive results and require careful interpretation in conjunction with the dog's clinical history and symptoms.
By leveraging these testing methods, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to accurately diagnose food allergies in dogs and develop tailored dietary plans to address and manage allergic reactions effectively. Understanding the nuances of each testing method empowers pet owners to make informed decisions about their dogs' health, ensuring they receive the necessary support and care to lead allergy-free and fulfilling lives.
Elimination Diet
The elimination diet is a fundamental method for diagnosing food allergies in dogs. This approach involves removing all potential allergens from the dog's diet and replacing them with novel protein and carbohydrate sources that the dog has not been previously exposed to. The rationale behind this method lies in the need to eliminate all potential triggers of allergic reactions, allowing for the identification of specific food allergens affecting the dog.
During the elimination diet phase, pet owners transition their dogs to a limited ingredient diet comprising novel protein sources such as venison, duck, rabbit, and kangaroo, along with alternative carbohydrate sources like sweet potatoes, peas, and tapioca. These novel ingredients are selected based on their minimal exposure in the dog's previous diet, reducing the likelihood of triggering allergic reactions.
The duration of the elimination diet typically spans 8 to 12 weeks, allowing sufficient time for the dog's system to adjust to the new dietary regimen and for any existing allergic symptoms to subside. Throughout this period, pet owners meticulously monitor their dogs for any improvements in symptoms, such as reduced itching, skin irritations, gastrointestinal disturbances, and overall well-being. The absence of allergic reactions during the elimination diet phase indicates a positive response to the novel ingredients, suggesting that the previous diet may have contained allergenic components.
Following the elimination phase, pet owners may reintroduce specific foods that were previously part of the dog's diet. This gradual reintroduction allows for the observation of any adverse reactions or recurrence of allergic symptoms, providing valuable insights into the specific food allergens affecting the dog. If the reintroduction of certain foods leads to the reappearance of allergic reactions, it helps pinpoint the allergenic ingredients responsible for the dog's adverse responses.
The elimination diet serves as a practical and informative method for identifying food allergens in dogs, enabling pet owners and veterinarians to make informed decisions about their pets' dietary needs. By carefully managing the elimination diet process and observing the dog's responses to novel and reintroduced foods, pet owners can gain valuable insights into their dogs' specific food allergies, paving the way for tailored dietary plans and effective management of allergic reactions.
This method empowers pet owners to take proactive measures in addressing their dogs' food allergies, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and care to lead healthy, allergy-free lives.
Blood Tests
Blood tests, particularly serum allergy testing, play a pivotal role in identifying food allergens affecting dogs. These tests offer valuable insights into the dog's immune response to specific food proteins, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of food allergies. By measuring the levels of specific antibodies, including immunoglobulin E (IgE), in the dog's blood, serum allergy testing provides essential information about the presence of food allergies and the potential allergens triggering allergic reactions in dogs.
During serum allergy testing, a blood sample is obtained from the dog and analyzed to assess the levels of antibodies, particularly IgE, in response to various food proteins. Elevated levels of specific antibodies indicate the dog's immune system's heightened reactivity to certain food allergens, shedding light on the potential triggers of allergic reactions. By identifying the specific food proteins eliciting an immune response, serum allergy testing enables pet owners and veterinarians to pinpoint the allergenic components in the dog's diet, facilitating targeted dietary management and alleviation of allergic symptoms.
Interpreting the results of blood tests, such as serum allergy testing, requires careful consideration of the dog's clinical symptoms, dietary history, and overall health. By correlating the antibody levels with the dog's allergic manifestations, veterinarians can make informed assessments regarding the specific food allergens affecting the dog. This comprehensive approach ensures that the diagnosis of food allergies is accurate and enables the development of tailored dietary plans to address and manage allergic reactions effectively.
While blood tests, including serum allergy testing, offer valuable insights into food allergies in dogs, it's essential to recognize that these tests are most effective when interpreted in conjunction with the dog's clinical history and symptoms. By leveraging the information obtained from blood tests and considering the broader context of the dog's health and dietary patterns, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to develop targeted strategies for managing food allergies and enhancing the overall well-being of their canine companions.
Blood tests, particularly serum allergy testing, serve as valuable tools in the diagnostic process, empowering pet owners and veterinarians to make informed decisions about their dogs' dietary needs and health. By harnessing the insights provided by blood tests, pet owners can take proactive measures to address their dogs' food allergies, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and care to lead healthy, allergy-free lives.
Skin Tests
Intradermal skin testing, commonly utilized to diagnose environmental allergies in dogs, can also be employed to identify food allergens affecting our canine companions. This testing method involves the injection of small amounts of food allergens into the dog's skin, followed by the observation of any resulting allergic reactions, such as redness or swelling. By assessing the dog's skin response to specific food allergens, veterinarians can gain valuable insights into the potential triggers of food allergies, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and management of allergic reactions in dogs.
While skin tests offer a direct means of evaluating the dog's skin reactivity to food allergens, it's important to approach the interpretation of results with caution. Skin tests may carry a risk of false-positive results, necessitating careful consideration of the dog's clinical history, symptoms, and overall health. By correlating the outcomes of skin tests with the dog's allergic manifestations, veterinarians can make informed assessments regarding the specific food allergens affecting the dog, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and tailored management strategies.
It's essential to recognize that skin tests, while informative, should be interpreted in conjunction with the broader context of the dog's health and dietary patterns. By leveraging the insights obtained from skin tests and considering the dog's clinical history, pet owners and veterinarians can collaborate to develop targeted strategies for managing food allergies effectively. This comprehensive approach ensures that the diagnosis of food allergies is accurate, enabling the implementation of tailored dietary plans to address and manage allergic reactions in dogs.
Skin tests serve as valuable tools in the diagnostic process, empowering pet owners and veterinarians to make informed decisions about their dogs' dietary needs and health. By harnessing the insights provided by skin tests, pet owners can take proactive measures to address their dogs' food allergies, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and care to lead healthy, allergy-free lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing food allergies in dogs are essential aspects of responsible pet ownership. The intricate nature of food allergies, characterized by immune system responses to specific food proteins, underscores the importance of accurate diagnosis and targeted management strategies. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of food allergies in dogs, pet owners can take proactive measures to support their furry companions' well-being.
The identification of common food allergens for dogs, including beef, dairy, wheat, egg, chicken, lamb, soy, fish, and artificial additives, provides valuable insights into potential triggers of allergic reactions. Armed with this knowledge, pet owners can make informed decisions about their dogs' diet, minimizing the risk of exposure to allergenic ingredients.
Furthermore, the availability of testing methods, such as the elimination diet, blood tests, and skin tests, empowers pet owners and veterinarians to accurately diagnose food allergies in dogs. The implementation of these testing methods, in conjunction with careful observation of the dog's clinical symptoms and dietary history, facilitates the identification of specific food allergens, paving the way for tailored dietary plans and effective management of allergic reactions.
The elimination diet, with its focus on novel protein and carbohydrate sources, serves as a practical approach to pinpointing food allergens, enabling pet owners to make informed decisions about their dogs' dietary needs. Additionally, blood tests, particularly serum allergy testing, offer valuable insights into the dog's immune response to specific food proteins, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of food allergies. Skin tests, while informative, require careful interpretation in the context of the dog's health and dietary patterns, contributing to a comprehensive approach to diagnosing food allergies in dogs.
By leveraging the knowledge gained from understanding food allergies in dogs and the available testing methods, pet owners can provide their canine companions with the necessary support and care to lead healthy, allergy-free lives. The proactive management of food allergies, informed by accurate diagnosis and tailored dietary plans, ensures that dogs can thrive without the burden of allergic reactions, fostering a fulfilling and vibrant bond between pets and their owners.