Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Causes A Yeast Ear Infection In Dogs

Eye and Ear Health
What Causes A Yeast Ear Infection In Dogs
Published: February 2, 2024
Learn about the causes of yeast ear infections in dogs and how to maintain their eye and ear health. Find tips to prevent and treat ear issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Yeast ear infections can be a common and uncomfortable issue for dogs. These infections, caused by the overgrowth of yeast in the ears, can lead to discomfort, itching, and pain for our furry friends. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of yeast ear infections in dogs to ensure the well-being of our canine companions.
Yeast ear infections, also known as otitis externa, occur when there is an overgrowth of yeast in the external ear canal. This overgrowth can lead to inflammation, irritation, and a buildup of waxy discharge in the ears, causing discomfort and potential complications if left untreated.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of yeast ear infections in dogs, shedding light on the common causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. By gaining a deeper understanding of this prevalent issue, pet owners can take proactive steps to safeguard their dogs' ear health and overall well-being.
Understanding the intricacies of yeast ear infections in dogs is the first step toward effectively addressing and managing this condition. With the right knowledge and proactive measures, we can ensure that our beloved canine companions enjoy optimal ear health and a high quality of life.
Understanding Yeast Ear Infections in Dogs
Yeast ear infections in dogs, medically referred to as otitis externa, are a prevalent and discomforting condition that affects many canine companions. These infections occur when there is an overgrowth of yeast, typically Malassezia pachydermatis, in the external ear canal. This overgrowth can lead to inflammation, irritation, and the accumulation of waxy discharge, resulting in discomfort and potential complications if left untreated.
The warm and moist environment of a dog's ear canal provides an ideal breeding ground for yeast and other microorganisms. When the balance of the ear canal's environment is disrupted, often due to factors such as allergies, moisture, ear anatomy, or underlying health conditions, it creates a conducive environment for yeast to proliferate. Additionally, excessive ear hair, ear mites, or foreign objects in the ear can contribute to the development of yeast ear infections.
Yeast ear infections can be particularly bothersome for dogs, causing symptoms such as itching, redness, foul odor, discharge, and discomfort when the ears are touched. Dogs may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as head shaking, ear scratching, or rubbing their ears against furniture or the floor. In severe cases, untreated yeast ear infections can lead to secondary bacterial infections or even damage to the ear canal and eardrum.
It's important for pet owners to recognize the signs of yeast ear infections in dogs and seek prompt veterinary care to address the issue effectively. Understanding the underlying causes and contributing factors of yeast ear infections is crucial in implementing preventive measures and providing appropriate treatment to alleviate the discomfort experienced by our furry companions.
By gaining a deeper understanding of yeast ear infections in dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to maintain their dogs' ear health and overall well-being. Through regular ear inspections, prompt veterinary attention, and preventive measures, we can help our canine friends enjoy a life free from the discomfort and complications associated with yeast ear infections.
Common Causes of Yeast Ear Infections
Yeast ear infections in dogs can stem from various factors that disrupt the natural balance of the ear canal environment, creating an ideal breeding ground for yeast overgrowth. Understanding the common causes of these infections is essential for pet owners to take proactive measures in safeguarding their dogs' ear health. Here are the primary factors contributing to yeast ear infections in dogs:
-
Moisture and Humidity: The warm and moist environment within a dog's ear canal provides an optimal setting for yeast proliferation. Activities such as swimming or bathing, especially in humid climates, can lead to moisture accumulation in the ears, creating a favorable environment for yeast growth.
-
Allergies: Dogs with underlying allergies, whether environmental or food-related, are more susceptible to yeast ear infections. Allergic reactions can lead to inflammation and changes in the ear canal environment, promoting yeast overgrowth.
-
Ear Anatomy: Certain breeds with floppy or hairy ears are predisposed to yeast ear infections due to reduced air circulation within the ear canal. Additionally, dogs with narrow ear canals may experience poor ventilation, creating an environment conducive to yeast proliferation.
-
Foreign Objects and Ear Mites: The presence of foreign objects, such as grass seeds or debris, in the ear canal can cause irritation and disrupt the natural balance, leading to yeast overgrowth. Ear mites, a common parasite in dogs, can also contribute to ear irritation and inflammation, increasing the risk of yeast infections.
-
Underlying Health Conditions: Dogs with compromised immune systems, endocrine disorders, or skin conditions are more prone to yeast ear infections. These underlying health issues can weaken the body's natural defenses, making it easier for yeast to proliferate in the ears.
-
Poor Ear Hygiene: Inadequate ear cleaning and maintenance can result in the accumulation of wax, debris, and moisture in the ear canal, creating an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth.
Understanding these common causes of yeast ear infections empowers pet owners to take proactive steps in preventing and addressing this discomforting condition. By minimizing exposure to moisture, addressing underlying allergies, maintaining proper ear hygiene, and seeking prompt veterinary care, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their dogs' ear health and overall well-being.
Symptoms of Yeast Ear Infections in Dogs
Yeast ear infections in dogs can manifest through a range of noticeable symptoms, signaling discomfort and potential complications within the ear canal. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for pet owners to seek timely veterinary care and address the underlying issue effectively. Here are the common symptoms of yeast ear infections in dogs:
-
Ear Scratching and Head Shaking: Dogs with yeast ear infections often exhibit persistent scratching of the affected ear(s) and vigorous head shaking as they attempt to alleviate the discomfort caused by the infection.
-
Ear Odor: A distinct, unpleasant odor emanating from the ears is a common indicator of yeast ear infections in dogs. This odor is often described as musty or yeasty and may be noticeable even from a distance.
-
Redness and Swelling: Inflamed and swollen ear canals are typical signs of yeast ear infections. The affected ears may appear red, inflamed, and tender to the touch, indicating the presence of an underlying issue.
-
Discharge: Dogs with yeast ear infections may experience the discharge of waxy, dark brown, or blackish material from the affected ears. This discharge can range from a thick, waxy consistency to a more liquid texture, depending on the severity of the infection.
-
Ear Sensitivity: Dogs may display signs of discomfort or sensitivity when their ears are touched or manipulated. This can manifest as reluctance to have the ears handled, increased head shyness, or a noticeable flinch when the ears are touched.
-
Behavioral Changes: Discomfort from yeast ear infections can lead to changes in a dog's behavior. They may exhibit signs of irritability, restlessness, or a reluctance to engage in activities that typically bring them joy.
-
Balance and Coordination Issues: In severe cases, yeast ear infections can affect a dog's balance and coordination. Pet owners may observe their dogs experiencing difficulty maintaining balance, stumbling, or displaying unsteady movements.
Recognizing these symptoms is pivotal in addressing yeast ear infections in dogs promptly. By seeking veterinary care at the first sign of these symptoms, pet owners can ensure that their canine companions receive the necessary treatment to alleviate discomfort and prevent potential complications associated with yeast ear infections.
Diagnosing Yeast Ear Infections
Diagnosing yeast ear infections in dogs requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical examination, diagnostic tests, and a thorough assessment of the dog's medical history. Veterinary professionals employ various techniques to accurately diagnose and differentiate yeast ear infections from other ear-related issues, ensuring appropriate treatment and management. The diagnostic process for yeast ear infections typically involves the following steps:
-
Physical Examination: A crucial initial step in diagnosing yeast ear infections involves a thorough physical examination of the dog's ears. Veterinary professionals carefully inspect the external ear canal and eardrum for signs of inflammation, redness, discharge, and odor. Additionally, they assess the dog's behavior and responses to ear manipulation to gauge discomfort and sensitivity.
-
Ear Cytology: Ear cytology, the microscopic examination of ear discharge, is a fundamental diagnostic tool for identifying yeast overgrowth in the ear canal. A sample of the ear discharge is collected and examined under a microscope to detect the presence of yeast organisms, such as Malassezia pachydermatis. This analysis provides valuable insights into the type and severity of the ear infection, guiding the selection of appropriate treatment.
-
Bacterial Culture and Sensitivity Testing: In cases where secondary bacterial infections are suspected or in recurrent or severe ear infections, veterinary professionals may conduct bacterial culture and sensitivity testing. This diagnostic approach involves culturing the ear discharge to identify the specific bacterial strains present and determine their susceptibility to various antibiotics. This information is crucial in formulating targeted and effective treatment plans.
-
Underlying Health Assessment: Since underlying health conditions can predispose dogs to yeast ear infections, veterinary professionals may conduct additional assessments to evaluate the dog's overall health. This may include blood tests, skin evaluations, and allergy testing to identify any contributing factors that need to be addressed to prevent recurrent infections.
Accurate diagnosis is paramount in effectively addressing yeast ear infections in dogs. By employing a combination of clinical examination, cytological analysis, and, if necessary, culture testing, veterinary professionals can tailor treatment plans to the specific characteristics of the infection, ensuring optimal outcomes for the affected dogs. Pet owners play a vital role in this process by promptly seeking veterinary care upon observing symptoms and providing comprehensive information about their dog's medical history, ultimately contributing to the accurate diagnosis and management of yeast ear infections.
Treatment Options for Yeast Ear Infections
Addressing yeast ear infections in dogs requires a multifaceted approach aimed at alleviating discomfort, resolving the underlying infection, and preventing recurrence. Veterinary professionals employ various treatment options tailored to the specific characteristics of the infection and the individual needs of the affected dogs. Here are the primary treatment options for yeast ear infections in dogs:
-
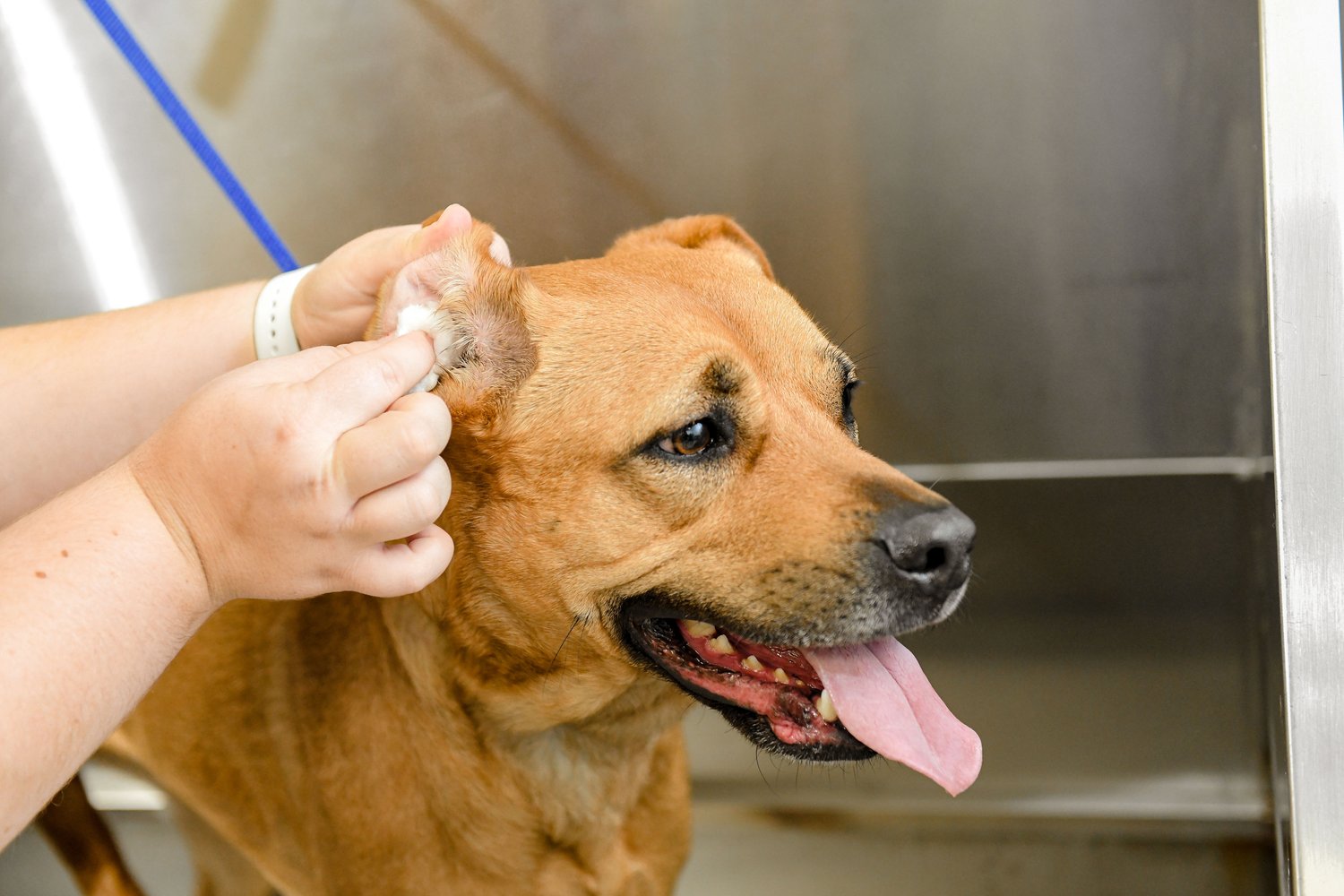
Ear Cleaning: Thorough ear cleaning is a fundamental aspect of managing yeast ear infections. Veterinary professionals perform gentle yet effective ear cleaning to remove accumulated wax, debris, and discharge from the ear canal. This not only facilitates the penetration of topical medications but also helps restore the natural balance of the ear environment.
-
Topical Antifungal Medications: Topical antifungal preparations, such as ear drops or ointments containing antifungal agents, are commonly prescribed to combat yeast overgrowth in the ear canal. These medications target the underlying yeast infection, reducing the population of yeast organisms and alleviating inflammation and discomfort.
-
Anti-inflammatory Medications: In cases of severe inflammation and discomfort, veterinary professionals may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling, redness, and pain within the ear canal. These medications help alleviate discomfort and create a more favorable environment for the effectiveness of antifungal treatments.
-
Systemic Antifungal Therapy: In recurrent or severe cases of yeast ear infections, systemic antifungal medications may be necessary. These oral medications target yeast overgrowth throughout the body, providing comprehensive treatment for systemic yeast infections that may contribute to recurrent ear issues.
-
Management of Underlying Conditions: Addressing underlying health conditions, such as allergies or immune system disorders, is crucial in preventing recurrent yeast ear infections. Veterinary professionals may recommend specific dietary changes, allergy management strategies, or immune-modulating therapies to address these underlying factors.
-
Follow-up Care and Monitoring: After initiating treatment, follow-up care and monitoring are essential to assess treatment response, ensure medication compliance, and detect any signs of recurrence. Veterinary professionals may schedule follow-up appointments to re-evaluate the ears, perform additional cytological examinations, and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
By combining these treatment options, veterinary professionals can effectively manage yeast ear infections in dogs, alleviate discomfort, and reduce the risk of recurrence. Pet owners play a pivotal role in the treatment process by diligently administering prescribed medications, maintaining proper ear hygiene, and adhering to veterinary recommendations for long-term management.
Through collaborative efforts between pet owners and veterinary professionals, dogs affected by yeast ear infections can receive comprehensive care, leading to improved ear health and a higher quality of life.
Preventing Yeast Ear Infections in Dogs
Preventing yeast ear infections in dogs is a proactive endeavor that involves implementing various measures to maintain optimal ear health and minimize the risk of recurrent infections. By addressing predisposing factors and adopting preventive strategies, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of their canine companions experiencing discomfort associated with yeast ear infections. Here are essential steps to prevent yeast ear infections in dogs:
-
Regular Ear Inspections: Conducting routine ear inspections is crucial for early detection of potential issues. Pet owners should examine their dogs' ears regularly, looking for signs of redness, swelling, excessive wax buildup, or unusual odor. Early identification of abnormalities allows for prompt veterinary intervention, preventing minor concerns from escalating into full-blown infections.
-
Ear Cleaning and Maintenance: Maintaining proper ear hygiene is paramount in preventing yeast ear infections. Regular, gentle cleaning of the ears helps remove accumulated wax, debris, and moisture, creating an unfavorable environment for yeast overgrowth. Pet-safe ear cleaning solutions recommended by veterinary professionals can aid in keeping the ear canal clean and minimizing the risk of infections.
-
Drying Ears After Water Exposure: After swimming or bathing, ensuring thorough drying of the ears is essential. Moisture accumulation in the ear canal creates an ideal breeding ground for yeast. Drying the ears with a soft towel or using a pet-safe ear drying solution helps prevent the onset of infections due to prolonged moisture exposure.
-
Allergy Management: Addressing underlying allergies, whether environmental or food-related, is pivotal in preventing recurrent yeast ear infections. Identifying and managing allergens that trigger allergic reactions can help reduce inflammation in the ear canal, minimizing the likelihood of yeast overgrowth.
-
Regular Grooming and Ear Hair Maintenance: For breeds with hairy or floppy ears, regular grooming and ear hair maintenance are essential. Trimming excess hair around the ears promotes better air circulation, reducing moisture retention and creating an environment less conducive to yeast proliferation.
-
Healthy Diet and Immune Support: Providing a balanced, high-quality diet and immune system support can contribute to overall health, including ear health. Proper nutrition and immune system support help bolster the body's natural defenses, reducing susceptibility to yeast infections.
-
Prompt Veterinary Care for Ear Issues: Any signs of ear discomfort or abnormalities should prompt immediate veterinary attention. Early intervention allows for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment, preventing the progression of minor ear concerns into more severe infections.
By incorporating these preventive measures into their canine care routine, pet owners can actively safeguard their dogs' ear health and minimize the occurrence of yeast ear infections. Proactive management and preventive strategies play a pivotal role in ensuring that our furry companions enjoy optimal ear health and a high quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, yeast ear infections in dogs can pose significant discomfort and potential complications, making it essential for pet owners to be well-informed about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures associated with this prevalent condition. By understanding the underlying factors contributing to yeast ear infections, such as moisture accumulation, allergies, ear anatomy, and underlying health conditions, pet owners can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of their canine companions experiencing this discomforting issue.
Recognizing the symptoms of yeast ear infections, including ear scratching, odor, redness, and discharge, empowers pet owners to seek prompt veterinary care, ensuring timely diagnosis and effective treatment. The diagnostic process, encompassing physical examination, ear cytology, and, if necessary, bacterial culture and sensitivity testing, plays a crucial role in accurately identifying yeast ear infections and tailoring treatment plans to the specific characteristics of the infection.
Treatment options, ranging from ear cleaning and topical medications to systemic antifungal therapy, aim to alleviate discomfort, resolve the underlying infection, and prevent recurrence. Through collaborative efforts between pet owners and veterinary professionals, dogs affected by yeast ear infections can receive comprehensive care, leading to improved ear health and a higher quality of life.
Furthermore, preventive measures, including regular ear inspections, proper ear hygiene, allergy management, and prompt veterinary care for any ear abnormalities, are instrumental in minimizing the likelihood of yeast ear infections. By integrating these preventive strategies into their canine care routine, pet owners can actively safeguard their dogs' ear health and reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Ultimately, by gaining a deeper understanding of yeast ear infections in dogs and implementing proactive measures, pet owners can play a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being and ear health of their beloved canine companions. Through vigilance, preventive care, and prompt intervention, we can strive to create a nurturing environment where our furry friends can thrive free from the discomfort and complications associated with yeast ear infections.
